最近看到一個多線程面試題,有三個線程分別打印A、B、C,請用多線程編程實現,在屏幕上循環打印10次ABCABC…
看到這個題目,首先想到的是解決方法是定義一個Integer類對象,初始化為0,由3個線程共享,如果Integer對象取余3之後等於0,則打印A,同時進行加1操作;如果Integer對象取3之後等於1,則打印B,同時進行加1操作;如果Integer對象取3之後等於1,則打印C,如果循環打印了10次的話,就退出線程。
/**
* ThreeThread
* 3個線程測試
*/
public class ThreeThread {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Integer gData = 0;
Thread thread1 = new MyTask(gData, 0, "A");
Thread thread2 = new MyTask(gData, 1, "B");
Thread thread3 = new MyTask(gData, 2, "C");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
thread3.join();
}
}
class MyTask extends Thread {
private Integer gData;
private int n;
private String info;
public MyTask(Integer gData, int n, String info) {
super("thread " + info);
this.gData = gData;
this.n = n;
this.info = info;
}
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while (true) {
synchronized (gData) {
if (gData % 3 == n) {
System.out.print(info + " ");
gData++;
i++;
}
}
if (i == 10) {
break;
}
else {
Thread.yield();
try {
sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
運行程序結果如下:
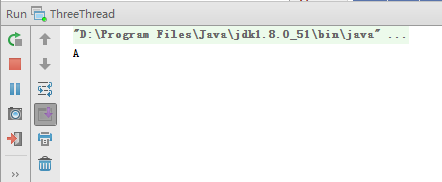
發現只有A線程打印了"A",並沒有發現B線程和C線程打印字符串:(。難道是A線程更改了Integer對象的值,而B線程和C線程並沒有“看到”更新後的值?於是,在線程類的run方法的while循環中增加代碼如下:
while (true) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + gData);
synchronized (gData) {
if (gData % 3 == n) {
System.out.print(info + " ");
gData++;
i++;
}
}
...
}
運行程序結果如下:
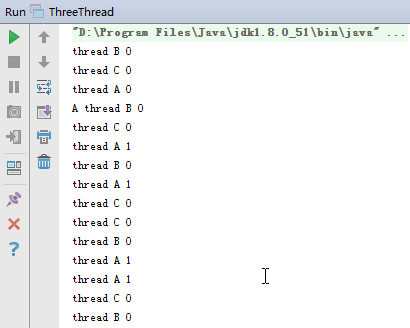
由運行結果可知,剛開始A、B、C線程都擁有Integer類變量,並且初值為0。當A線程更改Integer類變量為1時,但是B和C線程中的Integer類變量的值仍然為0,因此,結果肯定不會打印出ABCABC....
通過閱讀Integer類源碼,可知Integer類中存放int值的變量類型是final的:
/**
* The value of the {@code Integer}.
*
* @serial
*/
private final int value;
也就是說,Integer類對象的值每更新一次,就會創建一個新的Integer對象。運行程序結果只打印出了"A",表示剛開始A、B、C線程都擁有同一個Integer類變量,並且初值為0,但是當A線程更新Integer對象的值後,A線程中的Integer對象和B/C線程中的Integer對象已經不是同一個對象了。
為了能夠正常打印出ABCABC字符串,可以把Integer對象類型改為AtomicInteger,代碼如下:
/**
* ThreeThread
* 3個線程測試
*/
public class ThreeThread {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
AtomicInteger gData = new AtomicInteger(0);
Thread thread1 = new MyTask(gData, 0, "A");
Thread thread2 = new MyTask(gData, 1, "B");
Thread thread3 = new MyTask(gData, 2, "C");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
thread3.join();
}
}
class MyTask extends Thread {
private AtomicInteger gData;
private int n;
private String info;
public MyTask(AtomicInteger gData, int n, String info) {
super("thread " + info);
this.gData = gData;
this.n = n;
this.info = info;
}
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while (true) {
synchronized (gData) {
if (gData.get() % 3 == n) {
System.out.print(info + " ");
gData.incrementAndGet();
i++;
}
}
if (i == 10) {
break;
}
else {
Thread.yield();
try {
sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
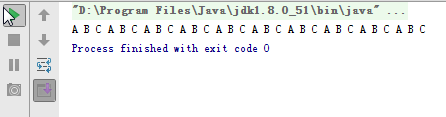
第二種打印ABCABC...字符串的解決方法是使用wait/notify函數,示例代碼如下:
/**
* ThreeThread2
* 三個線程依次輸出A B C,使用線程同步方式
*/
public class ThreeThread2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Object A = new Object();
Object B = new Object();
Object C = new Object();
MyThread myThread1 = new MyThread(C, A, "A");
MyThread myThread2 = new MyThread(A, B, "B");
MyThread myThread3 = new MyThread(B, C, "C");
myThread1.start();
Thread.sleep(10);
myThread2.start();
Thread.sleep(10);
myThread3.start();
try {
myThread1.join();
myThread2.join();
myThread3.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread {
private Object prev;
private Object curr;
private String info;
public MyThread(Object prev, Object curr, String info) {
this.prev = prev;
this.curr = curr;
this.info = info;
}
public void run() {
int cnt = 10;
while (cnt-- > 0) {
synchronized (prev) {
synchronized (curr) {
System.out.print(info + " ");
curr.notify();
}
try {
prev.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
