一、前言
Jdom是什麼?
Jdom是一個開源項目,基於樹形結構,利用純java的技術對XML文檔實現解析,生成,序列化以及多種操作。它是直接為java編程服務,利用java語言的特性(方法重載,集合),把SAX和DOM的功能結合起來,盡可能的把原來解析xml變得簡單,我們使用Jdom解析xml會是一件輕松的事情。
Jdom的優點:
1、Jdom專用於java技術,比Dom應用占用更少內存。
2、Jdom提供更加簡單和邏輯性訪問xml信息的基礎方法
3、除xml文件外,Jdom還可以訪問其他的數據源,例如可以創建類從SQL查詢結果中訪問數據
Jdom的構成:
Jdom由6個包構成
Element類表示XML文檔的元素
org.jdom: 解析xml文件所要用到的基礎類
org.jdom.adapters: 包含DOM適配的Java類
org.jdom.filter: 包含xml文檔的過濾類
org.jdom.input: 包含讀取XML文檔的Java類
org.jdom.output: 包含輸出XML文檔的類
org.jdom.trans form: 包含將Jdom xml文檔接口轉換為其他XML文檔接口的Java類
xml是什麼?
xml是一種廣為使用的可擴展標記語言,java中解析xml的方式有很多,最常用的像jdom、dom4j、sax等等。
Jdom包下載:http://www.jdom.org/downloads/index.html
這裡筆者代碼做的是使用java創建一個xml和讀取一個xml,僅作為筆記介紹。
二、操作
下載jdom包,解壓文件jdom-2.0.6.jar,jdom-2.0.6-javadoc.jar,將包導入到lib文件夾下。(注,如果有錯誤的話,將Jdom中的包全部導入)
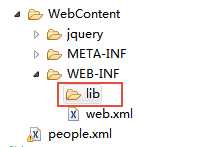
例子1:使用jdom創建一個xml文件,名字為people.xml
新建類CareateJdom
package com.book.jdom;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.jdom2.Document;
import org.jdom2.Element;
import org.jdom2.output.Format;
import org.jdom2.output.XMLOutputter;
//生成xml文件
public class CreateJdom {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定義元素
Element people,student;
people = new Element("people");
student = new Element("student");
//設置屬性
student.setAttribute("name", "張三");
student.setAttribute("salary","8000");
//設置文本
student.setText("呵呵");
//將其添加到根目錄下
people.addContent(student);
//新建一個文檔。
Document doc = new Document(people);
//讀取格式,賦值給當前的Format
Format format = Format.getCompactFormat();
//對當前格式進行初始化
format.setEncoding("UTF-8");
//設置xml文件縮進4個空格
format.setIndent(" ");
//建一個xml輸出工廠,將格式給工廠
XMLOutputter xmlout = new XMLOutputter(format);
try {
//將其寫好的文本給工廠,並且建一個文件輸出流,將數據輸出
xmlout.output(doc, new FileOutputStream("people.xml"));
System.out.println("成功!");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/*運行結果:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<people>
<student name="張三" salary="8000" />
</people>
* */
例子2:使用Jdom解析people.xml文件
新建Readxml類
package com.book.jdom;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import org.jdom2.Document;
import org.jdom2.Element;
import org.jdom2.JDOMException;
import org.jdom2.input.SAXBuilder;
//讀取people.xml文檔
public class Readxml {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//新建構造器解析xml
SAXBuilder sax = new SAXBuilder();
//建一個文檔去接受數據
Document doc;
try {
//獲取people.xml文檔
doc = sax.build("people.xml");
//獲得根節點
Element people = doc.getRootElement();
//獲得根節點下的節點數據
List<Element> list = people.getChildren();
for(int i = 0;i<list.size();i++){
Element e = list.get(i);
//獲得屬性值
System.out.println("name:"+e.getAttributeValue("name")+" salary:"+e.getAttributeValue("salary"));
//獲得文本值
System.out.println(e.getText());
}
} catch (JDOMException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/*
* 運行結果:
* name:張三 salary:8000
呵呵
* */
解析xml