一、動態方法調用(DMI:Dynamic Method Invocation)
⒈struts2中同樣提供了這個包含多個邏輯業處理的Action,這樣就可以在一個Action中進行多個業務邏輯處理。例如:當用戶通過不同的提交按鈕來提交同一個表單的時候,系統通過不同的方法來處理用戶不同的請求,這時候就需要讓同一個Action中包含有多個控制處理的邏輯。
⒉動態方法調用有:
①、改變struts.xml中的action中的method屬性。
②、改變form表單中的action屬性來改變不同提交的請求邏輯。
③、使用通配符。
二、簡單示例(改變form表單中的action屬性):
①、首先顯示一個表單,表單中有兩個提交按鈕,但分別代表不同的業務。當點擊登錄時用戶登錄;當點擊注冊時用戶注冊。
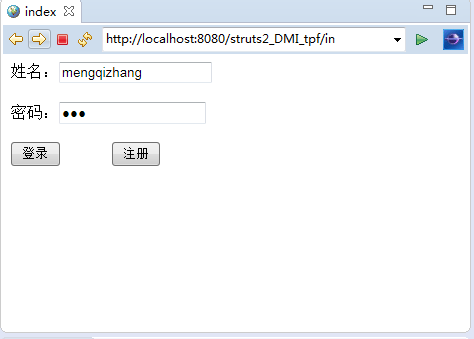
②、用戶登錄:
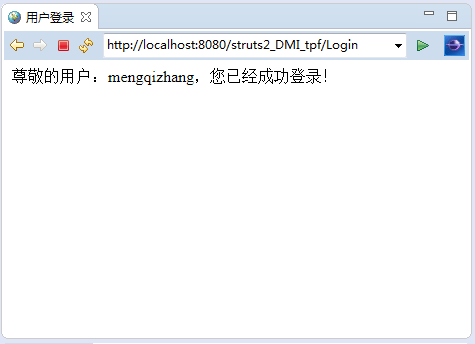
③、用戶注冊:
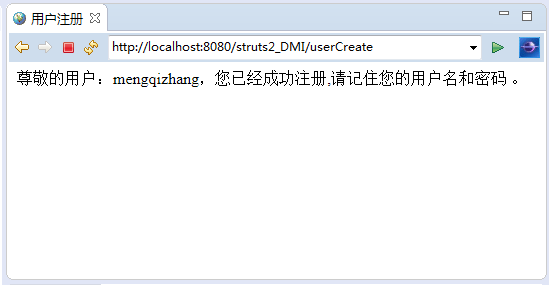
詳細代碼(本例子建立在struts2的基礎上的簡單例子,所以struts2的搭建在這裡不詳細演示,如果對struts2有疑問請求看:http://www.cnblogs.com/demoMeng/p/5841976.html):
①、登錄注冊的頁面(index.jsp):DMI中改變form表單中action屬性的方式的就下面的腳本段是關鍵,其他的struts.xml文件只要進行相關的配置即可。
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<script src="js/jquery-1.7.2.js"></script>
<title>index</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
$("input:eq(3)").click(function(){
//獲取表單並且改變action的屬性值
$("#form").attr("action","userCreate");
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form action="userLogin" method="post" id="form">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name" /><br><br>
密碼:<input type="password" name="password" /><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="登錄">
<input type="submit" value="注冊">
</form>
</body>
</html>
②、struts.xml:配置文件
<struts>
<package name="myP" extends="struts-default">
<action name="in" class="action.Action" method="go">
<result name="login">WEB-INF/jsp/index.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="userLogin" class="action.Action" method="test">
<result name="userLogin">WEB-INF/jsp/userLogin.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="userCreate" class="action.Action" method="create">
<result name="userCreate">WEB-INF/jsp/userCreate.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
③、Action類:
package action;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
public class Action extends ActionSupport {
private String name;
private String password;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String go(){
System.out.println("去登錄注冊頁面!!");
return "login";
}
public String test(){
System.out.println("用戶登錄");
return "userLogin";
}
public String create(){
System.out.println("用戶注冊");
return "userCreate";
}
}
本例子只是簡單的DMI中的一種方式,沒有加入過多的業務邏輯處理如:用戶登錄是否正確並且符合條件。只是一個簡單示例,具體實戰中需要使用到的業務需要進一步修改分析和完善,謝謝浏覽。