基本排序算法,排序算法
該部分是對算法(四)簡單排序的總結。
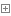
算法1、簡單選擇排序
基本思想:
是一種最簡單的排序算法,首先,找到數組中最小的那個元素,然後,將它和數組中的第一個元素交換位置。再次,在剩下的元素中找到最小的元素,將它與數組的第二個元素交換位置。如此往復,直到將整個數組排序。
算法特點:
![]()
1 package basic.sort;
2 /**
3 * 選擇排序
4 *
5 * Created by Evan on 2016-8-18.
6 */
7 public class SelectionSort {
8 public static void selectSort(int[] a) {
9 int i;
10 int j;
11 int temp = 0;
12 int flag = 0;
13 int n = a.length;
14 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
15 temp = a[i];
16 flag = i;
17 for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
18 if (a[j] < temp) {
19 temp = a[j];
20 flag = j;
21 }
22
23 }
24 System.out.println(j);
25 if (flag != i) {
26 a[flag] = a[i];
27 a[i] = temp;
28 }
29 }
30
31 }
32 public static void main(String[] args) {
33 int i = 0;
34 int a[] = {5,4,7,8,9,9,10,2,3,1};
35 selectSort(a);
36 for(i = 0; i< a.length;i++){
37 System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
38 }
39 }
40 }
SelectionSort
算法2、插入排序
基本思想:
將每一張牌插入到其他已經有序的牌中的適當位置。將其余元素在插入前都向右移動一位。
算法特點:
平均插入排序需要N2/4比較和N2/4交換,最壞情況下N2/2比較和N2/2交換,最好情況下需要N-1次比較和0次交換。適合對部分有序的數組排序。
時間復雜度最好為O(N),平均和最壞為O(N2),空間復雜度為O(1),穩定排序

![]()
1 package basic.sort;
2
3 import java.util.Arrays;
4
5 /**
6 * 插入排序
7 *
8 * Created by Evan on 2016-8-18.
9 */
10 public class InsertSort {
11 public static void insertSort(int[] a) {
12 if (a != null) {
13 for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
14 int temp = a[i];
15 int j = i;
16
17 while (j >= 1&&a[j - 1] > temp) {
18 a[j] = a[j - 1];
19 j--;
20 }
21
22 a[j] = temp;
23 }
24 }
25 }
26 public static void main(String []args){
27 int a[] = {5,4,7,8,9,10,9,2,3,1};
28 insertSort(a);
29 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
30 }
31 }
InsertSort
兩者比較:對於隨機排序的無重復主鍵的數組,插入排序和選擇排序的運行時間是平方級別的,兩者之比應該是一個較小的常數。
算法3、希爾排序
基本思想:
使數組中任意間隔為h的元素都是有序的。
算法特點:
在插入排序的基礎上,將移動元素的距離有1改為h,希爾排序高效的原因是它權衡了子數組的規模和有序性。排序之初,各個子數組都很短,排序之後,子數組都是部分有序的。子數組部分有序的程度取決於遞增序列的選擇。時間復雜度達不到平方級。空間復雜度為O(1),不穩定。

![]()
1 package basic.sort;
2
3 import java.util.Arrays;
4 /**
5 * 希爾排序
6 * 按升序排列
7 * Created by Evan on 2016-8-18.
8 */
9 public class ShellSort {
10 public static void sort(int a[]){
11 int N = a.length;
12 int h = 1;
13 while(h < N/3)
14 h = h * 3 + 1; //1,4,13,40,121,....
15 while(h >= 1){
16 for(int i = h; i < N; i++){
17 //將a[i]插入到a[i-h],a[i-2*h],a[i-3*h].....之中
18 for(int j = i;j >= h && a[j] < a[j - h]; j -= h){
19 int temp = a[j];
20 a[j] = a[j - h];
21 a[j - h] = temp;
22 }
23 }
24 h = h / 3;
25 }
26 }
27 public static void main(String []args) {
28 int[] nums = {2, 7, 8, 3, 1, 6, 9, 4, 5, 4};
29 ShellSort.sort(nums);
30 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
31 }
32 }
ShellSort
算法4、歸並排序
基本思想:
先遞歸的將它分成兩半分別排序,然後將結果歸並起來。
算法特點:
時間復雜度最好、最壞和平均復雜度為O(nlogn),空間復雜度為O(n),穩定排序。沒有任何基於比較的算法能夠保證使用少於lg(N!) ~ NlgN次比較將長度為N的數組排序。

![]()
1 package basic.sort;
2 /**
3 * 歸並排序
4 *
5 * Created by Evan on 2016-8-19.
6 */
7 public class MergeSort {
8 public static void Merge(int nums[], int low, int mid, int high) {
9 int[] temp = new int[high - low + 1];
10 int i = low;// 左指針
11 int j = mid + 1;// 右指針
12 int k = 0;
13
14 // 把較小的數先移到新數組中
15 while (i <= mid && j <= high) {
16 if (nums[i] < nums[j]) {
17 temp[k++] = nums[i++];
18 } else {
19 temp[k++] = nums[j++];
20 }
21 }
22
23 // 把左邊剩余的數移入數組
24 while (i <= mid) {
25 temp[k++] = nums[i++];
26 }
27
28 // 把右邊邊剩余的數移入數組
29 while (j <= high) {
30 temp[k++] = nums[j++];
31 }
32
33 // 把新數組中的數覆蓋nums數組
34 for (int k2 = 0; k2 < temp.length; k2++) {
35 nums[k2 + low] = temp[k2];
36 }
37 }
38
39 public static void MergeSort1(int a[], int l, int r) {
40 if (l < r) {
41 int mid = (l + r) / 2;
42 MergeSort1(a, l, mid);
43 MergeSort1(a, mid + 1, r);
44 Merge(a, l, mid, r);
45 }
46 }
47
48 public static void main(String[] args) {
49 int a[] = { 5, 4, 7, 8, 9, 5, 9, 2, 3, 1 };
50 MergeSort1(a, 0, a.length - 1);
51 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
52 System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
53 }
54 }
55 }
MergeSort
算法5、快速排序
基本思想:
將一個數組分層兩個子數組,將兩部分獨立地排序,快速排序和歸並排序是互補的:歸並排序將數組分層兩個子數組分別排序,並將有序的子數組歸並以將整個數組排序。而快速排序將數組排序的方式則是當兩個子數組都有序時整個數組也就自然有序了。
算法特點:
時間復雜度平均和最好為O(nlogn),最壞為O(N2),空間復雜度為O(1),不穩定排序。

![]()
1 package basic.sort;
2 /**
3 * 快速排序
4 */
5 import java.util.Arrays;
6
7 public class QuickSort {
8 public static int[] sort(int[] nums, int low, int high) {
9 if (low < high) {
10 int mid = partition(nums, low, high);
11 //左邊
12 sort(nums, low, mid - 1);
13 //右邊
14 sort(nums, mid + 1, high);
15 }
16 return nums;
17 }
18
19 public static int partition(int[] nums, int low, int high) {
20 int key = nums[low];//基准數
21 int i = low;//左指針
22 int j = high;//右指針
23
24 if (low < high) {
25 while (i < j) {
26 //形象點可以理解為,右指針左移
27 while (i < j && nums[j] >= key) {
28 j--;
29 }
30
31 if (i < j) {
32 nums[i] = nums[j];
33 i++;
34 }
35
36 //形象點可以理解為,左指針右移
37 while (i < j && nums[i] <= key) {
38 i++;
39 }
40
41 if (i < j) {
42 nums[j] = nums[i];
43 j--;
44 }
45 }
46
47 //把key填入最後的位置,即基准數位
48 nums[i] = key;
49 }
50 return i;
51 }
52
53 public static void main(String[] args) {
54 int[] nums = {2, 7, 8, 3, 1, 6, 9, 0, 5, 4};
55
56 QuickSort.sort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
57 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
58 }
59 }
QuickSort
算法6、堆排序
基本思想:
通過建堆和調整堆的方式,將數組排序。
算法特點:
時間復雜度最好,平均和最壞都是O(nlogn),空間復雜度為O(1)不穩定。

![]()
1 package basic.sort;
2
3 import java.util.Arrays;
4 /**
5 * 堆排序
6 * 降序
7 *
8 * Created by Evan on 2016-8-19.
9 */
10 public class HeapSort {
11
12 public static void MinHeapFixdown(int a[], int i, int n) {
13 int j, temp;
14
15 temp = a[i];
16 j = 2 * i + 1;
17 while (j < n) {
18 if (j + 1 < n && a[j + 1] < a[j]) // 在左右孩子中找最小的
19 j++;
20
21 if (a[j] >= temp)
22 break;
23
24 a[i] = a[j]; // 把較小的子結點往上移動,替換它的父結點
25 i = j;
26 j = 2 * i + 1;
27 }
28 a[i] = temp;
29 }
30
31 public static void MinheapsortTodescendarray(int a[], int n) {
32 for(int i = a.length / 2 - 1; i>= 0; i--){
33 MinHeapFixdown(a,i,a.length);
34 }
35 for (int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
36 int temp = a[0];
37 a[0] = a[i];
38 a[i] = temp;
39 MinHeapFixdown(a, 0, i);
40 }
41 }
42
43 public static void main(String[] args) {
44 int[] nums = { 2, 7, 8, 3, 1, 6, 9, 4, 5, 4 };
45
46 HeapSort.MinheapsortTodescendarray(nums, nums.length);
47 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
48 }
49 }
HeapSort
算法7、冒泡排序
基本思想:
兩兩比較,將較小的向上調整,較大的向下交換,較小的數就好比氣泡一樣向上浮動。
算法特點:
時間復雜度最好為O(n),平均和最壞為O(N2),空間復雜度O(1),穩定排序。

![]()
1 package basic.sort;
2
3 import java.util.Arrays;
4 /**
5 * 冒泡排序
6 *
7 * Created by Evan on 2016-8-18.
8 */
9 public class BubbleSort {
10 public static void bubbleSort(int[] a) {
11 int i;
12 int j;
13 int len = a.length;
14 int temp;
15 for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
16 for (j = 0; j + 1 < len - i && j < len - i; j++) {
17 if (a[j + 1] < a[j]) {
18 temp = a[j];
19 a[j] = a[j + 1];
20 a[j + 1] = temp;
21 }
22 }
23 }
24 }
25
26 public static void main(String[] args) {
27 int a[] = { 5, 4, 7, 8, 9, 5, 9, 2, 3, 1 };
28 bubbleSort(a);
29 /*for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
30 System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
31 }*/
32 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
33 }
34 }
BubbleSort
(未完待續)






