一、SpringMVC 使用 RequestMapping 來解決映射問題。
二、在學習 RequestMapping 之前,首先來看一張圖。
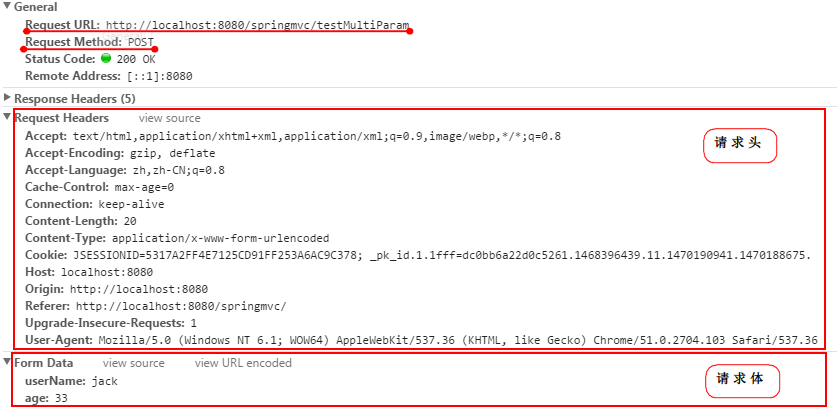
這張圖表示的是發送一次 http 請求時,所包含的請求 URL,請求 Method,以及請求頭和請求體。圖中已經標記的很明白了。
三、RequestMapping
1.翻譯過來是請求映射,在我看來,映射的是 http 請求和處理請求的 handler 方法。
2.@RequestMapping 可以標注於處理請求的 Handler 類定義處,也可以標注於 handler 方法定義處。
(1)標注於 Handler 類定義處:提供基礎的請求映射信息,相對於 web 應用的根目錄。在真實項目中,相當於 namespace 的作用,一般用來劃分模塊。如:
請求 URL:http://localhost:8080/springmvc/test/method
目標Handler:
/**
* @author solverpeng
* @create 2016-08-03-11:06
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class RequestMappingTest2 {
@RequestMapping("/method")
public String testRequestMapping() {
System.out.println("test requestMapping..");
return "success";
}
}
需要注意的是:此時 handler 方法處的 @RequestMapping value 屬性相對的是類定義處的路徑。
(2)標注於 handler 方法定義處:提供請求的映射信息,相對於 web 應用的根目錄。如:
請求URL:http://localhost:8080/springmvc/hello
目標 Handler:
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
System.out.println("hello springmvc!!!");
return "success";
}
3.@RequestMapping 屬性詳解。
在對各個屬性進行解釋說明之前,先來看看 @ReqeustMapping 這個注解類
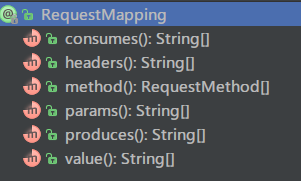
從中可以看出,SpringMVC 在 Servlet 環境下,可以對 http 請求的所有信息進行映射,並且通過數組的方式,同個規則下,可以映射多個。
(1)value 屬性
官方文檔是這樣解釋的:
The primary mapping expressed by this annotation.
<p>In a Servlet environment: the path mapping URIs (e.g. "/myPath.do").
Ant-style path patterns are also supported (e.g. "/myPath/*.do").
At the method level, relative paths (e.g. "edit.do") are supported
within the primary mapping expressed at the type level.
Path mapping URIs may contain placeholders (e.g. "/${connect}")
解釋的已經很明白了,在Servlet環境下,映射 URI,支持 Ant 風格的映射,在方法級別也支持相對路徑的映射。映射信息甚至可以從外部文件中獲取。
這裡對 Ant 風格進行說明:
Ant 風格資源地址支持 3 中匹配:
?:匹配一個字符
*:匹配任意個字符
**:匹配多層路徑
使用在 @RequestMapping 的 value 屬性中:
/test/*/add:匹配 /test/test01/add、/test/test02/add 等URL
/test/**/add:匹配 /test/springmvc/test01/add、/test/springmvc/test02/add 等 URL
/test/springmvc/add??:匹配 /test/springmvc/addaa、/test/springmvc/addbb 等 URL
具體使用:可以映射單個 uri ,也可以映射多個 uri。
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
System.out.println("hello springmvc!!!");
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping(value = {"/testUrl01", "/testUrl02"})
public String testRequestMappingUrl() {
System.out.println("test multi url...");
return "success";
}
(2)method 屬性
官方文檔是這樣解釋的:
The HTTP request methods to map to, narrowing the primary mapping:
GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE.
<p><b>Supported at the type level as well as at the method level!</b>
When used at the type level, all method-level mappings inherit
this HTTP method restriction (i.e. the type-level restriction
gets checked before the handler method is even resolved).
<p>Supported for Servlet environments as well as Portlet 2.0 environments.
簡單來說,method 屬性是對 http 請求方式的一種映射,主要映射 GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE 這幾種方式。
這幾種方式以枚舉的方式存放在:RequestMethod 枚舉類中:
public enum RequestMethod {
GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, TRACE
}
支持使用在類級別,也支持使用在方法級別,使用在類級別的時候,所有方法級別的映射都要繼承它。
具體使用:可以映射一個 method,也可以映射多個 method。
@RequestMapping(value = "/testMultiMethod", method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST})
public String testRequestMappingMultiMethod() {
System.out.println("test multi method...");
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/testUrl", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String testRequestMappingUrlAndMethod(){
System.out.println("test url and method...");
return "success";
}
(3)params 屬性
官方文檔解釋內容過多,這裡只做說明:
params 屬性映射的是請求參數,看下面幾種映射:
"myParam=myValue" style expressions:請求參數中必須包含 myParam 且值必須為 myValue。
"myParam!=myValue" style expressions:請求參數中必須包含 myParam 且值必須不為 myValue。
"!myParam" style expressions:請求參數中必須不能包含 myParam。
可以使用在類級別,也可以使用在方法級別。使用在方法級別,需要繼承自類級別。
看下面例子:
@RequestMapping(value = "/testMultiParam", params = {"userName", "age!=23"})
public String testRequestMappingParam5() {
System.out.println("test multi params ...");
return "success";
}
/**
* 請求參數中必須包含 userName 但是不能等於jack。
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/testParam4", params = "userName!=jack")
public String testRequestMappingParam4() {
System.out.println("test param4 ...");
return "success";
}
/**
* 請求參數中不能包含 userName。
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/testParam3", params = "!userName")
public String testRequestMappingParam3() {
System.out.println("test param3 ...");
return "success";
}
/**
* 請求參數必須為 userName,且值為 jack。否則會返回404錯誤
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/testParam2", params = "userName=jack")
public String testRequstMappingParam2() {
System.out.println("test param2 ...");
return "success";
}
/**
* 如果請求參數中沒有 userName 則會返回404錯誤
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/testParam", params = "userName")
public String testRequestMappingParam() {
System.out.println("test param...");
return "success";
}
(4)header 屬性
header 屬性用來映射 http 請求頭,主要分為下面幾種映射:
"My-Header=myValue":映射的請求頭屬性 My-Header 屬性值必須為 myValue,否則返回404。
"My-Header!=myValue":映射的請求頭屬性 My-Header 屬性值必須不為 myValue,否則返回404。
"!My-Header":映射的請求必須不能存在 My-Header 屬性,否則返回404。
如:
@RequestMapping(value = "/testHeader", headers = "Accept-Language=zh,zh-CN;q=0.8")
public String testRequestMappingHeader() {
System.out.println("test header ...");
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/testHeader", headers = "Accept-Language!=zh,zh-CN;q=0.8")
public String testRequestMappingHeader() {
System.out.println("test header ...");
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/testHeader", headers = "!Accept-Language")
public String testRequestMappingHeader() {
System.out.println("test header ...");
return "success";
}
同時支持媒體類型的通配,如:
RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers = "content-type=text/*")
將會匹配:"text/html", "text/plain" 等等。
(5)consumes 屬性
consumes 屬性用來映射消費者媒體類型,指的是請求,如:
consumes = "text/plain"
consumes = {"text/plain", "application/*"}
也可以使用 "!" 操作符,如在 "!text/plain" 中,用來過濾 Content-Type 除 "text/plain" 之外的類型。
Content-Type:請求頭的內容類型,表示發送到服務器的內容數據的媒體類型,在服務器端可以通過 request.getContentType() 的方式讀取。
使用 consumes = "text/plain" 表示只對 Content-Type 為 text/plain 的數據進行處理。即(消費請求內容數據)
(6)produces 屬性
produces 屬性用來映射生產者媒體類型,指的是響應,如:
produces = "text/plain"
produces = {"text/plain", "application/*"}
也可以使用 "!" 操作符,如在 "!text/plain" 中,用來過濾 Accept 除 "text/plain" 之外的類型。
在服務器端生產響應頭 Content-Type 並指定返回的數據(服務器端是生產者),客戶端是消費者。
總的來說:
①客戶端—發送請求—服務器:客戶端通過請求頭Content-Type指定內容體的媒體類型(即客戶端此時是生產者),服務器根據Content-Type消費內容體數據(即服務器此時是消費者)。
②服務器—發送請求—客戶端:服務器生產響應頭Content-Type指定的響應體數據(即服務器此時是生產者),客戶端根據Content-Type消費內容體數據(即客戶端此時是消費者)。
問題:
①服務器端可以通過指定【headers = "Content-Type=application/json"】來聲明可處理(可消費)的媒體類型,即只消費Content-Type指定的請求內容體數據。
②客戶端如何告訴服務器端它只消費什麼媒體類型的數據呢?即客戶端接受(需要)什麼類型的數據呢?服務器應該生產什麼類型的數據?此時我們可以請求的Accept請求頭來實現這個功能。
關於這兩個屬性,具體內容可以參考:
http://jinnianshilongnian.iteye.com/blog/1695047
四、總結:
本節沒有解釋 springmvc config文件和 web.xml 的配置,就以前一篇文章作為基礎。
SpringMVC 通過 RequestMapping 解決了 http 請求到目標處理方法的映射問題,通過 @RequestMapping 的各個屬性,包含了所有請求內容,甚至對特定的類型還分配了獨立的屬性,如映射消費者、生產者媒體類型。
在使用的過程中,這種寫法非常優雅、靈活。每一個屬性都是 String[] 形式,支持同時匹配多個值,屬於“或”的關系;且不同屬性之間同時存在的話,屬於“且”的關系。在學習該節之前,建議先對 http 請求有完整的理解。
已經在文章首頁對一個 http 請求通過一張圖的方式進行了說明。
還有一些基礎內容,可以參看:
http://www.cnblogs.com/solverpeng/p/5613568.html
還有關於 url-pattern 的問題,可以參看:
http://www.cnblogs.com/solverpeng/p/5729763.html