LinkedList是基於雙向循環鏈表(從源碼中可以很容易看出)實現的,除了可以當做鏈表來操作外,它還可以當做棧、隊列和雙端隊列來使用。
LinkedList同樣是非線程安全的,只在單線程下適合使用。
LinkedList實現了Serializable接口,因此它支持序列化,能夠通過序列化傳輸,實現了Cloneable接口,能被克隆。
以下是linkedList源碼(加入簡單代碼注釋):
/*
* @(#)LinkedList.java 1.67 06/04/21
*
* Copyright 2006 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.
* SUN PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*/
package java.util;
/**
* @author Josh Bloch
* @version 1.67, 04/21/06
* @see List
* @see ArrayList
* @see Vector
* @since 1.2
* @param <E> the type of elements held in this collection
*/
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
// 鏈表的表頭,表頭不包含任何數據。Entry是個鏈表類數據結構。
private transient Entry<E> header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);
// LinkedList中元素個數
private transient int size = 0;
// 默認構造函數:創建一個空的鏈表
public LinkedList() {
header.next = header.previous = header;
}
// 包含“集合”的構造函數:創建一個包含“集合”的LinkedList
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
// 獲取LinkedList的第一個元素
public E getFirst() {
if (size==0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 由於LinkedList是雙向鏈表;鏈表的表頭header中不包含數據。這裡返回header所指下一個節點所包含的數據。
return header.next.element;
}
// 獲取LinkedList的最後一個元素
public E getLast() {
if (size==0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 由於LinkedList是雙向鏈表;而表頭header不包含數據。這裡返回表頭header的前一個節點所包含的數據。
return header.previous.element;
}
// 刪除LinkedList的第一個元素
public E removeFirst() {
return remove(header.next);
}
// 刪除LinkedList最後一個元素
public E removeLast() {
return remove(header.previous);
}
// 添加元素到起始位置
public void addFirst(E e) {
addBefore(e, header.next);
}
// 添加元素到最後一個位置
public void addLast(E e) {
addBefore(e, header);
}
// 是否包含元素o
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
// LinkedList大小
public int size() {
return size;
}
// 將e添加到LinkedList中
public boolean add(E e) {
// 將節點(節點數據是e)添加到表頭(header)之前。即雙向鏈表的末端。
addBefore(e, header);
return true;
}
// 刪除元素o
// 從鏈表開始查找,如存在元素(o)則刪除該元素並返回true;否則,返回false。
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o==null) {
for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {
if (e.element==null) {
remove(e);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {
if (o.equals(e.element)) {
remove(e);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// 將“集合(c)”添加到LinkedList中。
// 實際上,是從雙向鏈表的末尾開始,將“集合(c)”添加到雙向鏈表中。
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
// 從雙向鏈表的index開始,將“集合(c)”添加到雙向鏈表中。
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+
", Size: "+size);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew==0)
return false;
modCount++;
// 設置“當前要插入節點的後一個節點”
Entry<E> successor = (index==size ? header : entry(index));
// 設置“當前要插入節點的前一個節點”
Entry<E> predecessor = successor.previous;
// 將集合(c)全部插入雙向鏈表中
for (int i=0; i<numNew; i++) {
Entry<E> e = new Entry<E>((E)a[i], successor, predecessor);
predecessor.next = e;
predecessor = e;
}
successor.previous = predecessor;
// 調整LinkedList的實際大小
size += numNew;
return true;
}
// 清空雙向鏈表
public void clear() {
Entry<E> e = header.next;
// 從表頭開始,逐個向後遍歷;對遍歷到的節點執行一下操作;
// (01) 設置前一個節點為null
// (02) 設置當前節點的內容為null
// (03) 設置後一個節點為“新的當前節點”
while (e != header) {
Entry<E> next = e.next;
e.next = e.previous = null;
e.element = null;
e = next;
}
header.next = header.previous = header;
size = 0;
modCount++;
}
// Positional Access Operations
// 返回LinkedList指定位置的元素
public E get(int index) {
return entry(index).element;
}
// 設置index位置對應的節點的值為element
public E set(int index, E element) {
Entry<E> e = entry(index);
E oldVal = e.element;
e.element = element;
return oldVal;
}
// 在index前添加節點,且節點的值為element
public void add(int index, E element) {
addBefore(element, (index==size ? header : entry(index)));
}
// 刪除index位置的節點
public E remove(int index) {
return remove(entry(index));
}
// 獲取雙向鏈表中指定位置的節點
private Entry<E> entry(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+
", Size: "+size);
Entry<E> e = header;
// 獲取index處的節點。
// 若index < 雙向鏈表長度的1/2,則從前先後查找;
// 否則,從後向前查找。
// 二分法查找
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++)
e = e.next;
} else {
for (int i = size; i > index; i--)
e = e.previous;
}
return e;
}
// Search Operations
// 從前向後查找,返回“值為對象(o)的節點對應的索引”
// 不存在就返回-1
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o==null) {
for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {
if (e.element==null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) {
if (o.equals(e.element))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 從後向前查找,返回“值為對象(o)的節點對應的索引”
// 不存在就返回-1
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o==null) {
for (Entry e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) {
index--;
if (e.element==null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Entry e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) {
index--;
if (o.equals(e.element))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
// Queue operations.
// 返回第一個節點
// 若LinkedList的大小為0,則返回null
public E peek() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return getFirst();
}
// 返回第一個節點
// 若LinkedList的大小為0,則拋出異常
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
// 刪除並返回第一個節點
// 若LinkedList的大小為0,則返回null
public E poll() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return removeFirst();
}
// 刪除並返回第一個節點
// 若LinkedList的大小為0,則拋出異常
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
// 將e添加雙向鏈表末尾
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
// Deque operations
// 將e添加雙向鏈表開頭
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
// 將e添加雙向鏈表末尾
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
// 返回第一個節點
// 若LinkedList的大小為0,則返回null
public E peekFirst() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return getFirst();
}
// 返回最後一個節點
// 若LinkedList的大小為0,則返回null
public E peekLast() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return getLast();
}
// 刪除並返回第一個節點
// 若LinkedList的大小為0,則返回null
public E pollFirst() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return removeFirst();
}
// 刪除並返回最後一個節點
// 若LinkedList的大小為0,則返回null
public E pollLast() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return removeLast();
}
// 將e插入到雙向鏈表開頭
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
// 刪除並返回第一個節點
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
// 從LinkedList開始向後查找,刪除第一個值為元素(o)的節點
// 從鏈表開始查找,如存在節點的值為元素(o)的節點,則刪除該節點
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
return remove(o);
}
// 從LinkedList末尾向前查找,刪除第一個值為元素(o)的節點
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o==null) {
for (Entry<E> e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) {
if (e.element==null) {
remove(e);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Entry<E> e = header.previous; e != header; e = e.previous) {
if (o.equals(e.element)) {
remove(e);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// 返回“index到末尾的全部節點”對應的ListIterator對象(List迭代器)
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
return new ListItr(index);
}
// List迭代器
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
// 上一次返回的節點
private Entry<E> lastReturned = header;
// 下一個節點
private Entry<E> next;
// 下一個節點對應的索引值
private int nextIndex;
// 期望的改變計數。用來實現fail-fast機制。
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
// 構造函數。
// 從index位置開始進行迭代
ListItr(int index) {
// index的有效性處理
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+
", Size: "+size);
// 若 “index 小於 ‘雙向鏈表長度的一半’”,則從第一個元素開始往後查找;
// 否則,從最後一個元素往前查找。
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
next = header.next;
for (nextIndex=0; nextIndex<index; nextIndex++)
next = next.next;
} else {
next = header;
for (nextIndex=size; nextIndex>index; nextIndex--)
next = next.previous;
}
}
// 是否存在下一個元素
public boolean hasNext() {
// 通過元素索引是否等於“雙向鏈表大小”來判斷是否達到最後。
return nextIndex != size;
}
// 獲取下一個元素
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (nextIndex == size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// next指向鏈表的下一個元素
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.element;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return nextIndex != 0;
}
// 是否存在上一個元素
public E previous() {
if (nextIndex == 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// next指向鏈表的上一個元素
lastReturned = next = next.previous;
nextIndex--;
checkForComodification();
return lastReturned.element;
}
// 獲取下一個元素的索引
public int nextIndex() {
return nextIndex;
}
// 獲取上一個元素的索引
public int previousIndex() {
return nextIndex-1;
}
// 刪除當前元素。
// 刪除雙向鏈表中的當前節點
public void remove() {
checkForComodification();
Entry<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next;
try {
LinkedList.this.remove(lastReturned);
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
if (next==lastReturned)
next = lastNext;
else
nextIndex--;
lastReturned = header;
expectedModCount++;
}
// 設置當前節點為e
public void set(E e) {
if (lastReturned == header)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
lastReturned.element = e;
}
// 將e添加到當前節點的前面
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
lastReturned = header;
addBefore(e, next);
nextIndex++;
expectedModCount++;
}
// 判斷 “modCount和expectedModCount是否相等”,依次來實現fail-fast機制。
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
// 雙向鏈表的節點所對應的數據結構。
// 包含3部分:上一節點,下一節點,當前節點值。
private static class Entry<E> {
// 當前節點值
E element;
// 下一節點
Entry<E> next;
// 上一節點
Entry<E> previous;
/**
* 鏈表節點的構造函數。
* @param element
* 當前節點值
* @param next
* 下一節點
* @param previous
* 上一節點
*/
Entry(E element, Entry<E> next, Entry<E> previous) {
this.element = element;
this.next = next;
this.previous = previous;
}
}
// 將節點(節點數據是e)添加到entry節點之前。
private Entry<E> addBefore(E e, Entry<E> entry) {
// 新建節點newEntry,將newEntry插入到節點e之前;並且設置newEntry的數據是e
Entry<E> newEntry = new Entry<E>(e, entry, entry.previous);
newEntry.previous.next = newEntry;
newEntry.next.previous = newEntry;
// 修改LinkedList大小
size++;
// 修改LinkedList的修改統計數:用來實現fail-fast機制。
modCount++;
return newEntry;
}
// 將節點從鏈表中刪除
private E remove(Entry<E> e) {
if (e == header)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
E result = e.element;
e.previous.next = e.next;
e.next.previous = e.previous;
e.next = e.previous = null;
e.element = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return result;
}
// 反向迭代器
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
return new DescendingIterator();
}
// 反向迭代器實現類。
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator {
final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());
// 反向迭代器是否下一個元素。
// 實際上是判斷雙向鏈表的當前節點是否達到開頭
public boolean hasNext() {
return itr.hasPrevious();
}
// 反向迭代器獲取下一個元素。
// 實際上是獲取雙向鏈表的前一個節點
public E next() {
return itr.previous();
}
// 刪除當前節點
public void remove() {
itr.remove();
}
}
// 克隆函數。返回LinkedList的克隆對象。
public Object clone() {
LinkedList<E> clone = null;
// 克隆一個LinkedList克隆對象
try {
clone = (LinkedList<E>) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError();
}
// 新建LinkedList表頭節點
clone.header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);
clone.header.next = clone.header.previous = clone.header;
clone.size = 0;
clone.modCount = 0;
// 將鏈表中所有節點的數據都添加到克隆對象中
for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next)
clone.add(e.element);
return clone;
}
// 返回LinkedList的Object[]數組
public Object[] toArray() {
Object[] result = new Object[size];
int i = 0;
for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next)
result[i++] = e.element;
return result;
}
// 返回LinkedList的模板數組。所謂模板數組,即可以將T設為任意的數據類型
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
// 若數組a的大小 < LinkedList的元素個數(意味著數組a不能容納LinkedList中全部元素)
// 則新建一個T[]數組,T[]的大小為LinkedList大小,並將該T[]賦值給a。
if (a.length < size)
a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(
a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
int i = 0;
// 將鏈表中所有節點的數據都添加到數組a中
Object[] result = a;
for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next)
result[i++] = e.element;
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 876323262645176354L;
// java.io.Serializable的寫入函數
// 將LinkedList的“容量,所有的元素值”都寫入到輸出流中
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultWriteObject();
// 寫入“容量”
s.writeInt(size);
// 將鏈表中所有節點的數據都寫入到輸出流中
for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next)
s.writeObject(e.element);
}
// java.io.Serializable的讀取函數:根據寫入方式反向讀出
// 先將LinkedList的“容量”讀出,然後將“所有的元素值”讀出
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject();
// 從輸入流中讀取“容量”
int size = s.readInt();
// 新建鏈表表頭節點
header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);
header.next = header.previous = header;
// 從輸入流中將“所有的元素值”並逐個添加到鏈表中
for (int i=0; i<size; i++)
addBefore((E)s.readObject(), header);
}
}
鏈表是由一系列非連續的節點組成的存儲結構,簡單分下類的話,鏈表又分為單向鏈表和雙向鏈表,而單向/雙向鏈表又可以分為循環鏈表和非循環鏈表,下面簡單就這四種鏈表進行圖解說明。
單向鏈表就是通過每個結點的指針指向下一個結點從而鏈接起來的結構,最後一個節點的next指向null。
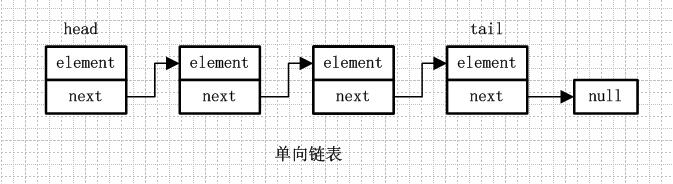
單向循環鏈表和單向列表的不同是,最後一個節點的next不是指向null,而是指向head節點,形成一個“環”。
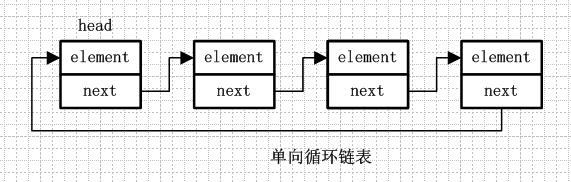
從名字就可以看出,雙向鏈表是包含兩個指針的,pre指向前一個節點,next指向後一個節點,但是第一個節點head的pre指向null,最後一個節點的tail指向null。
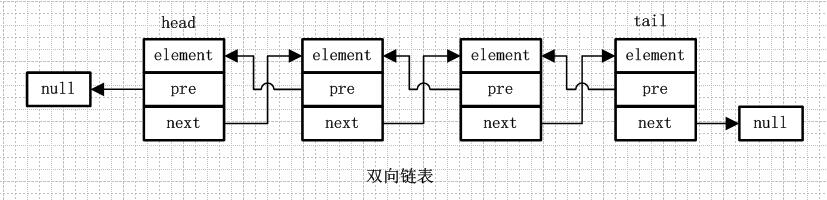
雙向循環鏈表和雙向鏈表的不同在於,第一個節點的pre指向最後一個節點,最後一個節點的next指向第一個節點,也形成一個“環”。而LinkedList就是基於雙向循環鏈表設計的。
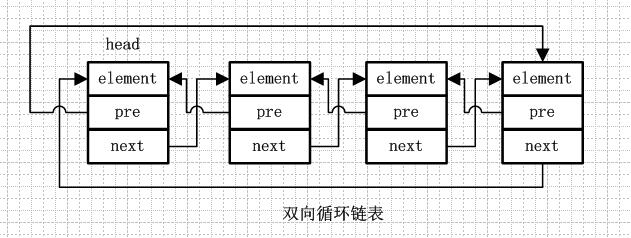
看一下LinkedList的定義部分:
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
可以看出LinkedList 繼承AbstractSequentialList 抽象類,實現了List,Deque,Cloneable,Serializable 幾個接口,AbstractSequentialList 繼承 AbstractList,是對其中方法的再抽象,其主要作用是最大限度地減少了實現受“連續訪問”數據存儲(如鏈接列表)支持的此接口所需的工作,簡單說就是,如果需要快速的添加刪除數據等,用AbstractSequentialList抽象類,若是需要快速隨機的訪問數據等用AbstractList抽象類。
Deque 是一個雙向隊列,也就是既可以先入先出,又可以先入後出,再直白一點就是既可以在頭部添加元素又在尾部添加元素,既可以在頭部獲取元素又可以在尾部獲取元素。看下Deque的源碼(已刪除注釋):
/*
* @(#)Deque.java 1.5 06/04/21
*
* Copyright 2006 Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.
* SUN PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*/
package java.util;
/**
* @author Doug Lea
* @author Josh Bloch
* @since 1.6
* @param <E> the type of elements held in this collection
*/
public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E> {
void addFirst(E e);
void addLast(E e);
boolean offerFirst(E e);
boolean offerLast(E e);
E removeFirst();
E removeLast();
E pollFirst();
E pollLast();
E getFirst();
E getLast();
E peekFirst();
E peekLast();
boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o);
boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o);
boolean add(E e);
boolean offer(E e);
E remove();
E poll();
E element();
E peek();
void push(E e);
E pop();
boolean remove(Object o);
boolean contains(Object o);
public int size();
Iterator<E> iterator();
Iterator<E> descendingIterator();
}
LinkedList總共有三個內部類,ListItr,Entry<E>和DescendingIterator,這三個內部類分別實現了List迭代器,雙向鏈表的節點所對應的數據結構和反向迭代器。
源碼在上面的代碼中已經給出,這裡不再給出,分析一下
ListItr(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+
", Size: "+size);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
next = header.next;
for (nextIndex=0; nextIndex<index; nextIndex++)
next = next.next;
} else {
next = header;
for (nextIndex=size; nextIndex>index; nextIndex--)
next = next.previous;
}
}
在這裡,這個構造函數只做了一件事情,就是加速查找,重點是這句話if (index < 0 || index > size)如果給出的index索引小於雙向鏈表長度的一半,則從頭向後查找,如果大於,則從尾向前查找。
這個內部類當中的其他方法這裡就不介紹了,set(),get(),add()等等這些方法,在最開始的注釋代碼中寫的很清晰了,這裡說其中的一個成員變量private int expectedModCount = modCount;
首先來看一下這個modCount是個什麼東西:它是LinkedList繼承的父類的父類AbstractList<E>中的一個成員變量protected transient int modCount = 0;它是用來記錄AbstractList結構性變化的次數。
在AbstractList的所有涉及結構變化的方法中都增加modCount的值,包括:add()、remove()、addAll()、removeRange()及clear()方法。這些方法每調用一次,modCount的值就加1。
而在這裡ListItr自己同時維護了一個expectedModCount,初始值是取的modCount,而當ListItr結構性變化的時候expectedModCount也會自動修改,包括next(),previous(),remove(),add(E e)等方法,而同樣在這些方法裡面的第一步都會去調用checkForComodification()這個方法進行修改的同步檢查,如果不同步將會拋出ConcurrentModificationException()這個異常。
Entry(E element, Entry<E> next, Entry<E> previous) {
this.element = element;
this.next = next;
this.previous = previous;
}
}
這個構造函數使用到了三個參數,分別是當前節點值,下一節點和上一節點。
在這個內部類中,實現了將將節點e添加到entry節點之前的這個方法,這個方法在LinkedList所有添加操作相關的方法中都調用了,源碼:
private Entry<E> addBefore(E e, Entry<E> entry) {
Entry<E> newEntry = new Entry<E>(e, entry, entry.previous);
newEntry.previous.next = newEntry;
newEntry.next.previous = newEntry;
size++;
modCount++;
return newEntry;
}
在這個方法一開始的地方就new了一個新的Entry對象出來,經典的雙向列表固定位置添加新節點,並且更新前驅結點的next域和後驅結點的previous域,並且將記錄操作數的modCount自增1。
反向迭代器實現類,這個類比較簡單,直接調用的ListItr的方法,在此不再贅述。
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
addBefore(e, header);
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
addBefore(element, (index==size ? header : entry(index)));
}
第一個add在尾部增加元素比較好理解:在header前添加元素e,header前就是最後一個結點,就是在最後一個結點的後面添加元素e;而第二個增加就不是那麼簡單了,同樣都是調用Entry的addBefore方法,第二個方法增加了一句判斷條件index==size ? header : entry(index),這個條件實際上的意思就是如果index等於list元素個數,則在隊尾添加元素(header之前),否則在index節點前添加元素。
到這裡可以發現一點,header作為雙向循環鏈表的頭結點是不保存數據的,也就是說hedaer中的element永遠等於null。
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified
* collection's iterator. The behavior of this operation is undefined if
* the specified collection is modified while the operation is in
* progress. (Note that this will occur if the specified collection is
* this list, and it's nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element
* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to
* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear
* in the list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element
* from the specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+
", Size: "+size);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew==0)
return false;
modCount++;
Entry<E> successor = (index==size ? header : entry(index));
Entry<E> predecessor = successor.previous;
for (int i=0; i<numNew; i++) {
Entry<E> e = new Entry<E>((E)a[i], successor, predecessor);
predecessor.next = e;
predecessor = e;
}
successor.previous = predecessor;
size += numNew;
return true;
}
第一個addAll方法是調用了第二個,仔細研究一下第二個addAll的方法,首先第一句話是越界檢查,第二局判斷是對添加的Collection做非0校驗,Entry<E> successor = (index==size ? header : entry(index));這句話的含義是:獲取要插入index位置的下一個節點,如果index正好是lsit尾部的位置那麼下一個節點就是header,否則需要查找index位置的節點,而Entry<E> predecessor = successor.previous;這句話的含義是:獲取要插入index位置的上一個節點,因為是插入,所以上一個點擊就是未插入前下一個節點的上一個。
private E remove(Entry<E> e) {
if (e == header)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
E result = e.element;
e.previous.next = e.next;
e.next.previous = e.previous;
e.next = e.previous = null;
e.element = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return result;
}
在這裡刪除本質上的意思就是前一節點和後一節點組合在一起就好了,互相修改一下前驅結點和後置節點
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the
* specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
Entry<E> e = entry(index);
E oldVal = e.element;
e.element = element;
return oldVal;
}
set方法看起來簡單了很多,只要修改該節點上的元素就好了。
/**
* Returns the indexed entry.
*/
private Entry<E> entry(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+
", Size: "+size);
Entry<E> e = header;
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++)
e = e.next;
} else {
for (int i = size; i > index; i--)
e = e.previous;
}
return e;
}
LinkedList是通過從header開始index計為0,然後一直往下遍歷(next),直到到底index位置。為了優化查詢效率,LinkedList采用了二分查找(這裡說的二分只是簡單的一次二分),判斷index與size中間位置的距離,采取從header向後還是向前查找。
基於雙向循環鏈表實現的LinkedList,通過索引Index的操作時低效的,index所對應的元素越靠近中間所費時間越長。而向鏈表兩端插入和刪除元素則是非常高效的(如果不是兩端的話,都需要對鏈表進行遍歷查找)。
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if this list contains
* at least one element <tt>e</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>.
*
* @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested
* @return <tt> true</tt> if this list contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o==null) {
for (Entry e = header .next; e != header; e = e.next ) {
if (e.element ==null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Entry e = header .next; e != header; e = e.next ) {
if (o.equals(e.element ))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size ;
if (o==null) {
for (Entry e = header .previous; e != header; e = e.previous ) {
index--;
if (e.element ==null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Entry e = header .previous; e != header; e = e.previous ) {
index--;
if (o.equals(e.element ))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
indexOf查詢元素位於容器的索引位置,都是需要對鏈表進行遍歷操作,也都是低效的操作,慎用。
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
* @return the head of this list, or <tt>null</tt> if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E peek() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return getFirst();
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list
* @return the head of this list, or <tt>null</tt> if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E poll() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return removeFirst();
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
/**
* Adds the specified element as the tail (last element) of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @since 1.5
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
// Deque operations
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the front of this list.
*
* @param e the element to insert
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Deque#offerFirst})
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the end of this list.
*
* @param e the element to insert
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Deque#offerLast})
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the first element of this list,
* or returns <tt>null</tt> if this list is empty.
*
* @return the first element of this list, or <tt>null</tt>
* if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E peekFirst() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return getFirst();
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the last element of this list,
* or returns <tt>null</tt> if this list is empty.
*
* @return the last element of this list, or <tt>null</tt>
* if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E peekLast() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return getLast();
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the first element of this list,
* or returns <tt>null</tt> if this list is empty.
*
* @return the first element of this list, or <tt>null</tt> if
* this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pollFirst() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return removeFirst();
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the last element of this list,
* or returns <tt>null</tt> if this list is empty.
*
* @return the last element of this list, or <tt>null</tt> if
* this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pollLast() {
if (size==0)
return null;
return removeLast();
}
/**
* Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list. In other
* words, inserts the element at the front of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addFirst}.
*
* @param e the element to push
* @since 1.6
*/
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
/**
* Pops an element from the stack represented by this list. In other
* words, removes and returns the first element of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirst()}.
*
* @return the element at the front of this list (which is the top
* of the stack represented by this list)
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
很簡單,邏輯都是基於上面講的鏈表操作的。
————————————————————————————————————————————————————
參考資料:
給jdk寫注釋系列之jdk1.6容器(2):LinkedList源碼解析
【Java集合源碼剖析】LinkedList源碼剖析