Web 項目一般給特定人群使用,有些是局域網用戶量不足1K的內部系統,也有些廣域網用戶上萬的中型項目,當然還有用戶上億的大型項目。
這些大大小小的 Web 項目都會有用戶登錄的存在,登錄後有特定的權限,訪問特定的資源。
未登錄的用戶無法訪問系統資源,這塊功能通常都是有 Filter 來進行的。
在 Filter 中進行自由服務的配置,可以使用戶在不登陸的情況下也能對特定資源進行訪問。
Filter 可以采用開源的第三方權限管理,比如 Shiro,Spring Security.......
小型項目中繼承 javax.servlet.Filter 接口簡單實現也是可行的方案。
最近項目中遇到一些服務需要用戶在未登錄的情況下,在其他移動設備上面進行操作。
怎樣保證暴露在外的服務堅不可摧呢?
本篇借自己一次相似需求的實現,來分享在實踐中遇到的問題和解決思路,僅當作拋磚引玉之用,文中如有什麼不妥,還望看客老爺拍磚。
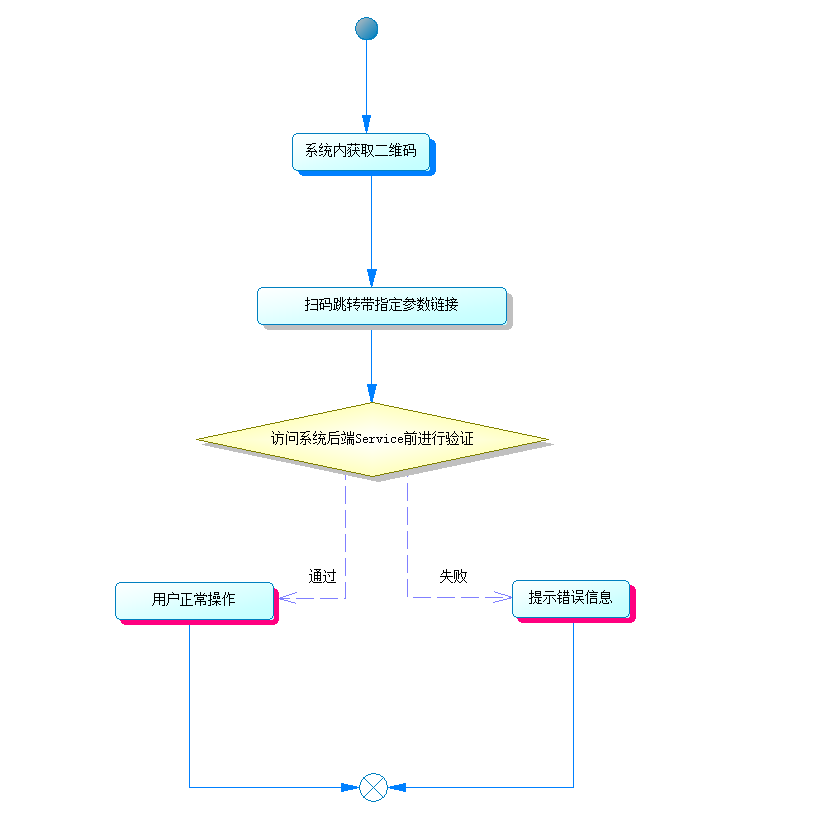
因為服務是在系統外用戶未登錄的情況下,在其他移動設備上面進行操作。
筆者這裡的"堅不可摧"主要是指在訪問後端 Service 前進行的兩次保證。
1.保證服務的安全性,只提供給正確的人,並且傳遞參數不能被其他人輕易獲取。
2.保證服務的即時性,每次生成的訪問鏈接,只能在有限的時間段內提供服務,避免其他人截獲該連接,在任何時間對該用戶的資源進行操作。
訪問鏈接的安全性保障,首當其中會想到鏈接後的參數加密。
加密的方式有很多中,首先得排除的是不可逆加密(MD5、SHA、HMAC......),畢竟解密後,都需要使用參數來做為操作的一些依據。
好的,接下來考慮雙向加密,因為是同一系統加密和解密,個人認為沒有必要使用非對稱加密算法。
最後將目光鎖定在了對稱加密,使用公共密鑰進行加密和解密(BASE64 確實是有點 low,直接抹殺掉)。
常用的對稱加密(DES、IDEA、RC2、RC4、SKIPJACK、RC5、AES..)中,根據項目要求或者自己喜好選用合適的算法。
至於加密算法的實現,我這裡沒有找第三方開源項目,使用的是 JDK 中 JCE 框架包。
如果你對 JCE 中算法實現感興趣,可以去讀讀源碼。
具體業務對稱加解密工具類實現:
如上述描述的,僅單純的保證了鏈接的安全性,還不能滿足當前項目要求。
還需要將每次生成的訪問鏈接,只能在有限的時間段內提供服務,避免其他人截獲該連接,在任何時間對該用戶的資源進行操作。
具體序列圖:
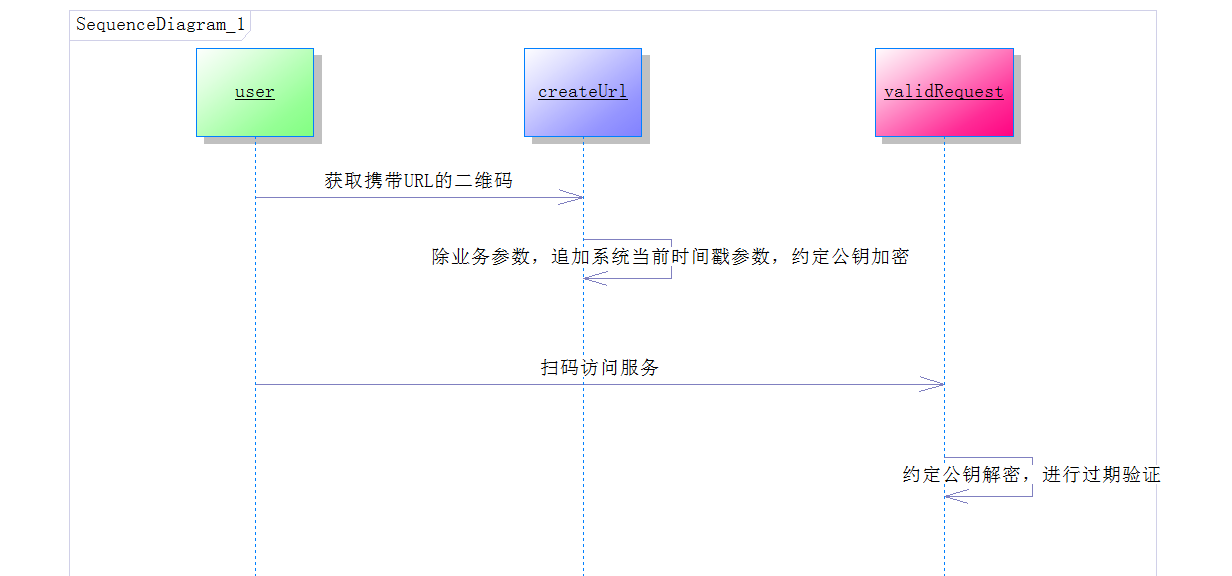
追加系統當前時間戳參數:
public static String encrypt(String parm1, String pam2) {
String resStr = null;
try {
EncryptionDecryption des = new EncryptionDecryption("定義的公鑰");
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(parm1) && StringUtil.isNotEmpty(pam2)) {
resStr = des.encrypt(parm1 + "," + pam2 + "," + DateFormatUtils.format(new Date(),"yyyyMMddHHmm"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return resStr;
}
在項目中最小粒度判斷到分鐘既可以,當然你也可以根據具體需求將時間戳粒度調整到秒或者毫秒級別。
約定公鑰解密,進行過期驗證:
private Boolean hasInvalidRequest(String param) {
EncryptionDecryption encryptionDecryption = new EncryptionDecryption("定義的公鑰");
String requestDate = encryptionDecryption.decrypt(param).split(",")[5];
if (requestDate.length() != 12) {
return Boolean.TRUE;
}
Date nowDate = new Date();
int nowTime_yyyyMMdd = Integer.parseInt(DateFormatUtils.format(nowDate, "yyyyMMdd"));
int requestTime_yyyyMMdd = Integer.parseInt(requestDate.substring(0, 8));
if (nowTime_yyyyMMdd > requestTime_yyyyMMdd) {
return Boolean.TRUE;
}
int nowTime_HHmm = Integer.parseInt(DateFormatUtils.format(nowDate, "HHmm"));
int requestTime_HHmm = Integer.parseInt(requestDate.substring(8));
if (nowTime_HHmm - requestTime_HHmm > Configutil.getConfig("valid_request_time")) {
return Boolean.TRUE;
}
return Boolean.FALSE;
}
判斷長度,判斷年月日,判斷分秒,這裡轉為 Int 沒有用Float 對比的原因,其一是不好駕馭,其二是代碼不簡潔。
有效的時間間隔,放到配置文件當中,因為這裡是需求變動的敏感點,統一配置,代碼不動,方便管理。