知識點:
我們平時看到的spring項目請求都是*.do的,但是像下面這兩個網址一樣,我們可以去掉.do,這樣看起來就比較清爽。第一個是比較明顯的REST風格URL,顯示的網址沒有後綴,第二種其實也算是一種REST風格URL。
效果預覽:可以看到地址欄上的url已經沒有.do了。
再點擊"文章一"可見:直接用文章的id顯示文章的地址。
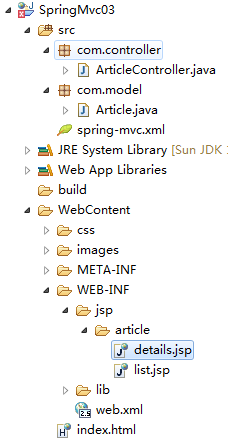
首先配置web.xml文件,為所有的地址請求spring攔截。
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 使用注解的包,包括子集 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com"/>
<!-- 視圖解析器 -->
<bean id="viewResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/article")
public class ArticleController {
@RequestMapping("/list")
public String list(Model model){
return "article/list";
}
@RequestMapping("/details/{id}")
public ModelAndView details(@PathVariable("id") int id){
ModelAndView mav=new ModelAndView();
if(id==1){
mav.addObject("article", new Article("文章一","這裡是文章一的內容"));
}else if(id==2){
mav.addObject("article", new Article("文章二","這裡是文章二的內容"));
}
mav.setViewName("article/details");
return mav;
}
}
注解:@PathVariable和@RequestParam,從名字上就可以看出來,他們分別是從路徑裡面去獲取變量,也就是把路徑當做變量,後者是從請求裡面獲取參數。
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<th colspan="2">
文章列表
</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>1</td>
<td>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/article/details/1" target="_blank">文章一</a>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>2</td>
<td>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/article/details/2" target="_blank">文章二</a>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
注解:這裡將文章一的路徑寫成/details/1,然後controller中就將1這個參數綁定到id上,再通過@PathVariable獲取這個1。
<body>
<p>${article.title }</p>
<p>${article.content }</p>
</body>
上面的DEMO是在沒有靜態資源的情況下的rest風格,但是實際情況下是有的,一般js,css,img,都會有,在上面的demo中,如果添加圖片或者其他東西是行不通的,因為在web.xml中將所有的請求都添加了過濾器。這個時候就需要我們對靜態資源做一步處理了。
Spring對靜態資源的處理是通過<mvc:resources …來處理,具體解釋就自己百度。
在上述DEMO的基礎上添加如下代碼:
<mvc:resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/images/"/>
<mvc:resources mapping="/resources2/**" location="/css/"/>
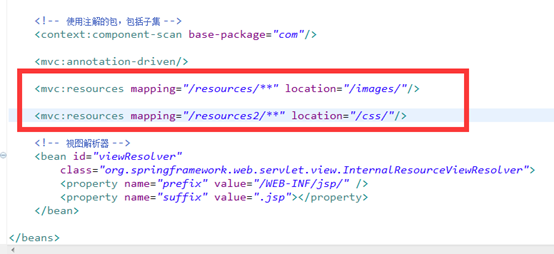
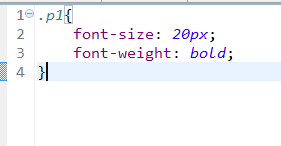
然後添加img和css, 這裡我添加一個img圖,和一個類css.具體css如下圖代碼:
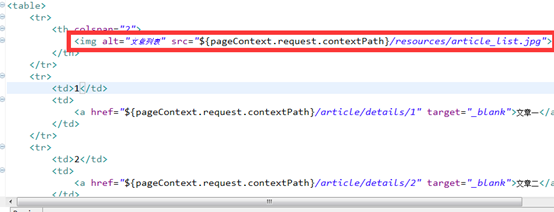
然後修改list.jsp。將圖片引用過來。
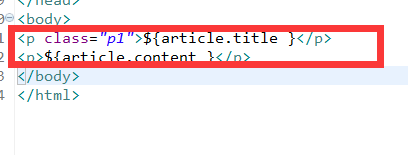
接著為details.jsp的文章內容,添加css.
測試:,
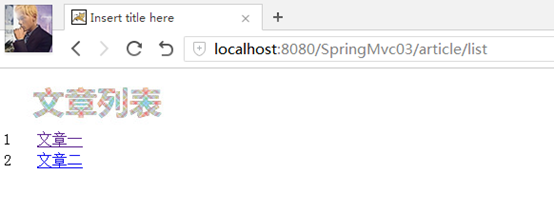
可以看到圖片顯示出來了,如果沒有對靜態資源進行處理的話,是不會顯示的。然後再點擊文章一,也可以看到文章一的標題是有變化了的。
好記性不如爛筆頭,菜鳥邊學邊把學到的東西記錄下來。