順序存儲對空間利用率較低,所以,二叉樹一般采用鏈式存儲結構,用一個鏈表來存儲一顆二叉樹。二叉鏈表至少包含3個域:數據域data,左指針域lchild和右指針域rchild,如果再加上一個指向雙親結點的指針就變成了三叉鏈表。
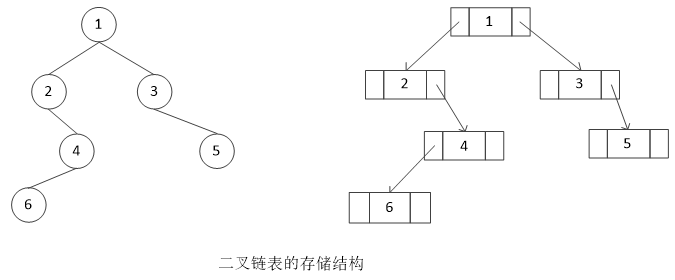
二叉樹的鏈式存儲結構如下:
/**
* 二叉鏈表結點
* @author cyhe
*/
private class Node{
Integer data;
Node lchild, rchild;
}
根據完全二叉樹的序列遞歸創建二叉樹,輸入序列時不存在的結點用0代替,以下是創建的代碼和一些有用的方法。
/**
* 存儲先序輸入的二叉樹,默認大小為10,當超過10自動調用resize方法擴容
*/
private Integer[] nodes = new Integer[10];
public LinkBiTree(){
init();
}
/**
* 獲取根節點
* @return
*/
public Node getRoot(){
return root;
}
/**
* 滿了自動擴容
* @param max
*/
private void resize(int max){
Integer[] temp = new Integer[max];
for(int i=0; i<nodes.length; i++){
temp[i] = nodes[i];
}
nodes = temp;
}
/**
* 先序輸入二叉樹,不存在的結點使用0
*/
public void init(){
System.out.println("先序列輸入一個二叉樹,不存在的結點用0代替,使用逗號隔開:");
// String[] ins = StdIn.readString().split(",");
String[] ins = "1,2,3,4,0,5,7,8".split(",");
n = ins.length;
for (int i = 0; i < ins.length; i++) {
if(i>=nodes.length){
resize(2 * nodes.length); // 擴大兩倍
}
nodes[i] = Integer.valueOf(ins[i]);
}
System.out.println("LinkBiTree [nodes=" + Arrays.toString(nodes) + "]");
root = build(1); // 遞歸創建樹
System.out.println("輸入的樹高度為:"+depth(root));
print();
}
/**
* 遞歸創建一顆樹, 使用完全二叉樹序列
* @param node
* @param data
*/
public Node build(int index){
if (index > n) {
return null;
}
Integer tmp = nodes[index - 1]; // 獲取結點的值
if (tmp == 0) { // 若為 0 表示結點不存在
return null;
} else {
Node node = new Node();
node.data = tmp;
node.lchild = build(2 * index); // 創建左子樹
node.rchild = build(2 * index + 1); // 創建右子樹
return node;
}
}
/**
* 遞歸獲取二叉樹的高度
* @return
*/
public int depth(Node node){
if(node != null){
int l = depth(node.lchild); // 左子樹高度
int r = depth(node.rchild); // 右子樹高度
return l > r ? l + 1 : r + 1; // 樹的高度為子樹最大高度加上根節點
}
return 0; // 空樹高度為0
}
/**
* 層次遍歷,利用隊列是實現
*/
public void levelOrder(Node root){
RingBuffer<Node> queue = new RingBuffer<Node>(n+1);
queue.put(root); // 根節點先進隊列
while(queue.size()>0){
Node tmp = queue.get();
System.out.print(tmp.data + " "); // 根
if (tmp.lchild != null) { // 如果根節點的左子樹存在,把左子樹編號入棧
queue.put(tmp.lchild);
}
if (tmp.rchild != null) { // 如果根節點的右子樹存在,把右子樹編號入棧
queue.put(tmp.rchild);
}
}
}
/**
* 遞歸先序遍歷
*/
public void preOrderRecur(Node node){
if(node != null){
System.out.print(node.data+" "); // 根
preOrderRecur(node.lchild); // 左
preOrderRecur(node.rchild); // 右
}
}
實現方法1:
/**
* 非遞歸先序遍歷
*/
public void preOrder(Node node){
ArrayStack<Node> stack = new ArrayStack<Node>(n + 1);
stack.push(node);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node tmp = stack.pop();
System.out.print(tmp.data + " "); // 根
if (tmp.rchild != null) { // 如果根節點的右子樹存在,把右子樹編號入棧
stack.push(tmp.rchild);
}
if (tmp.lchild != null) { // 如果根節點的左子樹存在,把左子樹編號入棧
stack.push(tmp.lchild);
}
}
}
實現方法2:
/**
* 非遞歸先序遍歷
*/
public void preOrderOne(Node node){
ArrayStack<Node> stack = new ArrayStack<Node>(n + 1);
while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(node != null){ // 把最左側的全部入棧
System.out.print(node.data + " "); // 根
stack.push(node);
node = node.lchild;
}
Node tmp = stack.pop(); // 彈出最後入棧的左子樹
node = tmp.rchild; // 看它有沒有右孩子
}
}
/**
* 遞歸中序遍歷
*/
public void inOrderRecur(Node node){
if(node != null){
inOrderRecur(node.lchild); // 左
System.out.print(node.data+" "); // 根
inOrderRecur(node.rchild); // 右
}
}
/**
* 非遞歸中序遍歷
*/
public void inOrder(Node node){
ArrayStack<Node> stack = new ArrayStack<Node>(n + 1);
while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(node != null){ // 把最左側的全部入棧
stack.push(node);
node = node.lchild;
}
Node tmp = stack.pop(); // 彈出最後入棧的左子樹
System.out.print(tmp.data + " "); // 先訪問左子樹
node = tmp.rchild; // 看它有沒有右孩子
}
}
/**
* 遞歸後序遍歷
*/
public void postOrderRecur(Node node){
if(node != null){
postOrderRecur(node.lchild); // 左
postOrderRecur(node.rchild); // 右
System.out.print(node.data+" "); // 根
}
}
/**
* 非遞歸後序遍歷
*/
public void postOrder(Node node){
ArrayStack<Node> stack = new ArrayStack<Node>(n + 1);
Node pre = null; // 前一個訪問的結點
while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while(node != null){ // 把最左側的全部入棧
stack.push(node);
node = node.lchild;
}
Node tmp = stack.peek(); // 現在要判斷棧內結點有沒有右孩子,或者右孩子是否訪問過
// 如果當前結點不存在右孩子或者右孩子已經訪問過,則訪問當前結點
if(tmp.rchild == null || pre == tmp.rchild){
Node n = stack.pop();
System.out.print(n.data + " "); // 訪問結點
pre = n;
} else {
node = tmp.rchild; // 否則訪問右孩子
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkBiTree<Integer> biTree = new LinkBiTree<Integer>();
System.out.print("先序遍歷(遞歸):");
biTree.preOrderRecur(biTree.getRoot());
System.out.print("\n中序遍歷(遞歸):");
biTree.inOrderRecur(biTree.getRoot());
System.out.print("\n後序遍歷(遞歸):");
biTree.postOrderRecur(biTree.getRoot());
System.out.print("\n層次遍歷:");
biTree.levelOrder(biTree.getRoot());
System.out.print("\n先序遍歷(非遞歸):");
// biTree.preOrder(biTree.getRoot());
biTree.preOrderOne(biTree.getRoot());
System.out.print("\n中序遍歷(非遞歸):");
biTree.inOrder(biTree.getRoot());
System.out.print("\n後序遍歷(非遞歸):");
biTree.postOrder(biTree.getRoot());
}
