工程的build.gradle中添加
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath "io.realm:realm-gradle-plugin:0.88.3"
}
}
引用module的build.gradle中添加
apply plugin: 'realm-android'
-keep class io.realm.annotations.RealmModule
-keep @io.realm.annotations.RealmModule class *
-keep class io.realm.internal.Keep
-keep @io.realm.internal.Keep class * { *; }
-dontwarn javax.**
-dontwarn io.realm.**
必須屬性和null值
在某些情況下,存在null值是不合理的. @Required可以聲明Boolean, Byte, Short, Integer, Long, Float, Double, String, byte[], Date,不能為null. 當其他類型使用@Required,會導致編譯錯誤. Fields with primitive types and the RealmList type are required implicitly.(必須通過setter和getter,否則不會獲取到正確數據) RealmObject不需要默認值@Ignore來聲明Realm忽略的屬性
和ios一樣
顧名思義當一個數據的內容改變時,它會自動更新該數據的所有實例化對象
realm.beginTransaction();
Dog myDog = realm.createObject(Dog.class);
myDog.setName("Fido");
myDog.setAge(1);
realm.commitTransaction();
Dog myPuppy = realm.where(Dog.class).equals("age", 1).findFirst();
realm.beginTransaction();
myPuppy.setAge(2);
realm.commitTransaction();
myDog.getAge(); // => 2
當數據變化,需要更新界面時,需要配合 [Realm notifications](#Realm notifications) 實現,後續會詳細描述這功能
@Index 來修飾索引類型
索引支持類型
Indexing a property will greatly speed up queries where the property is compared for equality (i.e. the = and IN operators), at the cost of slower insertions.
使用索引增加查詢速度的代價是插入數據時速度會降低
@PrimaryKey 用來修飾主鍵.@PrimaryKey可以修飾String,short,int,long.
@PrimaryKey只能修飾一個屬性.
@PrimaryKey聲明一個主鍵後,該屬性會被隱性聲明成@Index.
@PrimaryKey聲明一個主鍵後,該屬性會被隱性聲明成@Required,不能為null.
聲明主鍵之後,對象將被允許查詢,更新速度更加高效,並且要求每個對象保持唯一性。
一旦帶有主鍵的對象被添加到 Realm 之後,該對象的主鍵將不可修改。
當調用Realm.createObject(),它會返回一個有默認值的對象,當有主鍵時,主鍵會被設置默認值,這樣可能會與已有對象沖突.所以最好使用copyToRealm()或者copyToRealmOrUpdate()替換
MyObject obj = new MyObject();
obj.setId(42);
obj.setName("Fish");
realm.beginTransaction();
// This will create a new one in Realm
// realm.copyToRealm(obj);
// This will update a existing one with the same id or create a new one instead
realm.copyToRealmOrUpdate(obj);
realm.commitTransaction();
重寫 Object.ignoredProperties() 可以防止 Realm 存儲數據模型的某個屬性。Realm 將不會干涉這些屬性的常規操作,它們將由成員變量(ivar)提供支持,並且您能夠輕易重寫它們的 setter 和 getter。
class Person: Object {
dynamic var tmpID = 0
var name: String { // read-only properties are automatically ignored
return "\(firstName) \(lastName)"
}
dynamic var firstName = ""
dynamic var lastName = ""
override static func ignoredProperties() -> [String] {
return ["tmpID"]
}
}
Realm不支持final,transient和volatile修飾
public class Email extends RealmObject {
private String address;
private boolean active;
// ... setters and getters left out
}
public class Contact extends RealmObject {
private String name;
private Email email;
// ... setters and getters left out
}
public class Contact extends RealmObject {
private Email email;
// Other fields…
}
如果將email設為null,會斷開2個實例間的關系,但是email實例沒有被刪除
class Person: Object {
public class Contact extends RealmObject {
private RealmList emails;
// Other fields…
}
}
public class Person extends RealmObject {
private String id;
private String name;
private RealmList dogs;
// getters and setters
}
public class Dog extends RealmObject {
private String id;
private String name;
private String color;
// getters and setters
}
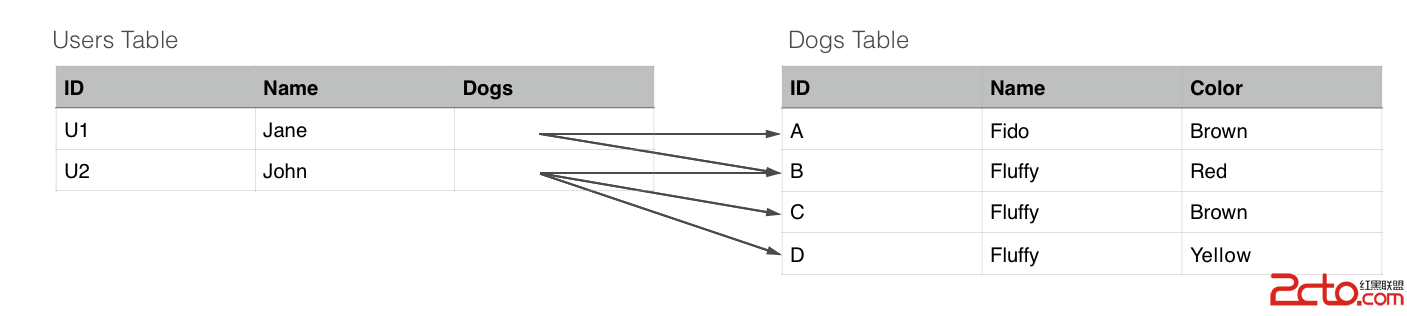
// users => [U1,U2]
RealmResults users = realm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("dogs.color", "Brown")
.findAll();
// r1 => [U1,U2]
RealmResults r1 = realm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("dogs.name", "Fluffy")
.equalTo("dogs.color", "Brown")
.findAll();
// r2 => [U2]
RealmResults r2 = realm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("dogs.name", "Fluffy")
.findAll()
.where()
.equalTo("dogs.color", "Brown")
.findAll();
.where()
.equalTo("dogs.color", "Yellow")
.findAll();
所有寫入操作(添加,修改,刪除)都必須依托一個write transaction.
由於write transaction會占用一定的資源,所以盡量精簡write transaction的個數.當隊列寫入時,只需要一個就write transaction
在UI線程和後台線程同時開始寫事務時,會導致ARN
寫事務都是線程安全的.
// Obtain a Realm instance
Realm realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance();
realm.beginTransaction();
//... add or update objects here ...
realm.commitTransaction();
當開始寫操作後,可以隨時取消
realm.beginTransaction();
User user = realm.createObject(User.class);
// ...
realm.cancelTransaction();
由於RealmObjects必須依賴在Realm,所以其創建方式如下:
realm.beginTransaction();
User user = realm.createObject(User.class); // Create a new object
user.setName("John");
user.setEmail("john@corporation.com");
realm.commitTransaction();
//========other
User user = new User("John");
user.setEmail("john@corporation.com");
// Copy the object to Realm. Any further changes must happen on realmUser
realm.beginTransaction();
User realmUser = realm.copyToRealm(user);
realm.commitTransaction();
當使用realm.copyToRealm後,對原始數據修改,將不會被同步到Realm中.
會自動執行realm.beginTransaction(), realm.commitTransaction()
realm.executeTransaction(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(Realm realm) {
User user = realm.createObject(User.class);
user.setName("John");
user.setEmail("john@corporation.com");
}
});
異步事務,主要是用於大量數據寫入
realm.executeTransactionAsync(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(Realm bgRealm) {
User user = bgRealm.createObject(User.class);
user.setName("John");
user.setEmail("john@corporation.com");
}
}, new Realm.Transaction.OnSuccess() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
// Transaction was a success.
}
}, new Realm.Transaction.OnError() {
@Override
public void onError(Throwable error) {
// Transaction failed and was automatically canceled.
}
});
RealmAsyncTask transaction = realm.executeTransactionAsync(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(Realm bgRealm) {
User user = bgRealm.createObject(User.class);
user.setName("John");
user.setEmail("john@corporation.com");
}
}, null);
public void onStop () {
if (transaction != null && !transaction.isCancelled()) {
transaction.cancel();
}
}
通過查詢操作,Realm 將會返回包含 Object 集合的Results實例。Results 的表現和 List 十分相似。
所有的查詢(包括查詢和屬性訪問)在 Realm 中都是延遲加載的,只有當屬性被訪問時,才能夠讀取相應的數據。也就是說當沒有使用數據前,進行多次排序或者過濾都是不需要額外cpu時間的
查詢結構不是Copy對象,而是引用對象.所以在Write操作中修改查詢數據,是直接修改數據庫中的數據.
Realm使用Fluent interface,也就是流接口
基本查詢語句
// Build the query looking at all users:
RealmQuery query = realm.where(User.class);
// Add query conditions:
query.equalTo("name", "John");
query.or().equalTo("name", "Peter");
// Execute the query:
RealmResults result1 = query.findAll();
// Or alternatively do the same all at once (the "Fluent interface"):
RealmResults result2 = realm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("name", "John")
.or()
.equalTo("name", "Peter")
.findAll();
當查詢內容為空時,RealmResults不會為null,它的size==0
主要是or()和not()
not(),用來否定花括號中的條件
流接口中支持”花括號”,beginGroup() => ‘{’ , endGroup() => ‘}’
RealmResults r = realm.where(User.class)
.greaterThan("age", 10) //implicit AND
.beginGroup()
.equalTo("name", "Peter")
.or()
.contains("name", "Jo")
.endGroup()
.findAll();
RealmResults result = realm.where(User.class).findAll();
result.sort("age"); // Sort ascending
result.sort("age", Sort.DESCENDING);
RealmResults teenagers = realm.where(User.class).between("age", 13, 20).findAll();
User firstJohn = teenagers.where().equalTo("name", "John").findFirst();
RealmResults teensWithPups = realm.where(User.class).between("age", 13, 20).equalTo("dogs.age", 1).findAll();
結果會自動更新
RealmResults puppies = realm.where(Dog.class).lessThan("age", 2).findAll();
puppies.size(); // => 0
realm.beginTransaction();
Dog dog = realm.createObject(Dog.class);
dog.setName("Fido");
dog.setAge(1);
realm.commitTransaction();
puppies.size(); // => 1
realm.allObjects()
RealmResults results = realm.where(User.class).findAll();
long sum = results.sum("age").longValue();
long min = results.min("age").longValue();
long max = results.max("age").longValue();
double average = results.average("age");
long matches = results.size();
RealmResults results = realm.where(User.class).findAll();
for (User u : results) {
// ... do something with the object ...
}
RealmResults results = realm.where(User.class).findAll();
for (int i = 0; i < results.size(); i++) {
User u = results.get(i);
// ... do something with the object ...
}
// Find all dogs older than or equal to 2 and change their age to 1
RealmResults results = realm.where(Dog.class).greaterThanOrEqualTo("age", 2).findAll();
realm.beginTransaction();
for (int i = results.size() -1; i >=0; i--) {
results.get(i).setAge(1);
}
realm.commitTransaction();
// obtain the results of a query
RealmResults results = realm.where(Dog.class).findAll();
// All changes to data must happen in a transaction
realm.beginTransaction();
// remove single match
results.remove(0);
results.removeLast();
// remove a single object
Dog dog = results.get(5);
dog.removeFromRealm();
// Delete all matches
results.clear();
realm.commitTransaction()
private RealmChangeListener callback = new RealmChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onChange() { // called once the query complete and on every update
// use the result
}
};
public void onStart() {
RealmResults result = realm.where(User.class).findAllAsync();
result.addChangeListener(callback);
}
public void onStop () {
result.removeChangeListener(callback); // remove a particular listener
// or
result.removeChangeListeners(); // remove all registered listeners
}
當RealmResults有數據綁定後,result.isLoaded(),會一直返回true
RealmResults result = realm.where(User.class).findAllAsync();
if (result.isLoaded()) {
// Results are now available
}
強制執行異步查詢,會阻塞當前線程.
RealmResults result = realm.where(User.class).findAllAsync();
result.load() // be careful, this will block the current thread until it returns
異步查詢只能使用在有Looper的線程上,否則會拋出異常.
Realm.setDefaultConfiguration()直接設置默認配置
Realm默認會將文件存儲在Context.getFilesDir(),文件路徑是無法修改的
// The RealmConfiguration is created using the builder pattern.
// The realm file will be located in Context.getFilesDir() with name "myrealm.realm"
RealmConfiguration config = new RealmConfiguration.Builder(context)
.name("myrealm.realm")
.encryptionKey(getKey())
.schemaVersion(42)
.setModules(new MySchemaModule())
.migration(new MyMigration())
.build();
// Use the config
Realm realm = Realm.getInstance(config);
RealmConfiguration myConfig = new RealmConfiguration.Builder(context)
.name("myrealm.realm").
.schemaVersion(2)
.setModules(new MyCustomSchema())
.build();
RealmConfiguration otherConfig = new RealmConfiguration.Builder(context)
.name("otherrealm.realm")
.schemaVersion(5)
.setModules(new MyOtherSchema())
.build();
Realm myRealm = Realm.getInstance(myConfig);
Realm otherRealm = Realm.getInstance(otherConfig);
public class MyApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
// The realm file will be located in Context.getFilesDir() with name "default.realm"
RealmConfiguration config = new RealmConfiguration.Builder(this).build();
Realm.setDefaultConfiguration(config);
}
}
public class MyActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Realm realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance();
// ... Do something ...
realm.close();
}
}
內存中的Realms,沒有保存在磁盤上.
優點:可以快速的訪問數據,而不需要考慮數據持久化的性能開銷.內存Realms只會在temp路徑裡存放幾個文件,用來進行線程間數據同步,不會將Realms中任何數據寫入磁盤中
不需要建立基於RealmObject類,只需要通過字符串來操作.
主要優勢是靈活
RealmConfiguration realmConfig = new RealmConfiguration.Builder(context).build();
DynamicRealm realm = DynamicRealm.getInstance(realmConfig);
// In a DynamicRealm all objects are DynamicRealmObjects
DynamicRealmObject person = realm.createObject("Person");
// All fields are accesssed using strings
String name = person.getString("name");
int age = person.getInt("age");
// An underlying schema still exists, so accessing a field that does not exist
// will throw an exception
person.getString("I don't exist");
// Queries stil work normally
RealmResults persons = realm.where("Person")
.equalTo("name", "John")
.findAll();
protected Void doInBackground(Void... params) {
Realm realm = null;
try {
realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance();
// ... Use the Realm instance
} finally {
if (realm != null) {
realm.close();
}
}
return null;
}
在有Looper的線程中,應該如下使用:
public class MyThread extends Thread {
private Realm realm;
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
try {
realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance();
//... Setup the handlers using the Realm instance
Lopper.loop();
} finally {
if (realm != null) {
realm.close();
}
}
}
}
在minSdkVersion >= 19時,可以如下使用:
try (Realm realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance()) {
// No need to close the Realm instance manually
}
在有Looper的線程上(包括UI線程)會自動更新.
可以使用isAutoRefresh()來知曉是否當前Realm是否支持自動刷新
這一章主要是講多線程開發,大量寫入事務最好是放在其他線程中,以防止UI線程被阻塞
只在一個線程中處理所有事情,不需要擔心並發和多線程.(然並卵的話)
Realm在多線程處理上不需要使用線程鎖,只需要注意寫入操作需要在Write事件中.
// in a Fragment or Activity, etc
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// ... boilerplate omitted for brevity
realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance();
// get all the customers
RealmResults customers = realm.where(Customer.class).findAllAsync();
// ... build a list adapter and set it to the ListView/RecyclerView/etc
// set up a Realm change listener
changeListener = new RealmChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onChange() {
// This is called anytime the Realm database changes on any thread.
// Please note, change listeners only work on Looper threads.
// For non-looper threads, you manually have to use Realm.refresh() instead.
listAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged(); // Update the UI
}
};
// Tell Realm to notify our listener when the customers results
// have changed (items added, removed, updated, anything of the sort).
customers.addChangeListener(changeListener);
}
// In a background service, in another thread
public class PollingService extends Service {
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Realm realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance();
// go do some network calls/etc and get some data and stuff it into a 'json' var
String json = customerApi.getCustomers();
realm.beginTransaction();
realm.createObjectFromJson(Customer.class, json); // Save a bunch of new Customer objects
realm.commitTransaction();
// At this point, the data in the UI thread is already up to date.
// ...
}
// ...
}
在其他類型的線程上操作,都是基於Snapshots.
UI線程或者其他添加Runloop的線程上,數據都會自動刷新,除非將Realm.autorefresh設置為NO
其他類型的線程,都是以最後一次修改成功的Realm為snapshot,除非是手動refresh
Realm, RealmObject or RealmResults不能進行多線程傳遞.
最好使用asynchronous query和asynchronous transaction
```
##Schemas
可以讓Realm只包含特定類型.
// Create the module
@RealmModule(classes = { Person.class, Dog.class })
public class MyModule {
}
// Set the module in the RealmConfiguration to allow only classes defined by the module.
RealmConfiguration config = new RealmConfiguration.Builder(context)
.setModules(new MyModule())
.build();
// It is possible to combine multiple modules to one schema.
RealmConfiguration config = new RealmConfiguration.Builder(context)
.setModules(new MyModule(), new MyOtherModule())
.build();
###Sharing schemas
```基於Library開發時,需要注意Realm必須expose並且Realm必須設置對應的schema.
如果不設置schema,當你使用它們時,會拋出異常.
// Library must create a module and set library = true. This will prevent the default
// module from being created.
// allClasses = true can be used instead of listing all classes in the library.
@RealmModule(library = true, allClasses = true)
public class MyLibraryModule {
}
// Library projects are therefore required to explicitly set their own module.
RealmConfiguration libraryConfig = new RealmConfiguration.Builder(context)
.name("library.realm")
.setModules(new MyLibraryModule())
.build();
// Apps can add the library RealmModule to their own schema.
RealmConfiguration config = new RealmConfiguration.Builder(context)
.name("app.realm")
.setModules(Realm.getDefaultModule(), new MyLibraryModule())
.build();
支持導入類型String,JSONObject,JSONArray和InputStream.
// A RealmObject that represents a city
public class City extends RealmObject {
private String city;
private int id;
// getters and setters left out ...
}
// Insert from a string
realm.beginTransaction();
realm.createObjectFromJson(City.class, "{ city: \"Copenhagen\", id: 1 }");
realm.commitTransaction();
// Insert from a JSONObject
realm.beginTransaction();
realm.createObjectFromJson(City.class, jsonObject);
realm.commitTransaction();
// Insert from a JSONArray
realm.beginTransaction();
realm.createObjectFromJson(City.class, jsonArray);
realm.commitTransaction();
// Insert multiple items using a InputStream
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("path_to_file"));
realm.beginTransaction();
try {
realm.createAllFromJson(City.class, is);
realm.commitTransaction();
} catch (IOException e) {
realm.cancelTransaction();
}
修改Listeners只會在有Looper的線程(包含UI線程)中回調,其他線程只能使用Realm.refresh()來刷新
在多線程中修改數據,有Looper的線程(包含UI線程)都會收到Listeners的回調
public class MyActivity extends Activity {
private Realm realm;
// A reference to RealmChangeListener needs to be held to avoid being
// removed by the garbage collector.
private RealmChangeListener realmListener;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance();
reamlListener = new RealmChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onChange() {
// ... do something with the updates (UI, etc.) ...
}};
realm.addChangeListener(realmListener);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
// Remove the listener.
realm.removeChangeListener(realmListener);
// Close the realm instance.
realm.close();
}
}
關閉所有Listeners
realm.removeAllChangeListeners();
RealmObject和RealmResults都可以添加Listeners
public class MyActivity extends Activity {
private Realm realm;
private RealmChangeListener puppiesListener;
private RealmChangeListener dogListener;
private RealmResults puppies;
private Dog dog;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
realm = Realm.getDefaultInstance();
puppiesListener = new RealmChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onChange() {
// ... do something with the updated puppies instance
}};
// Find all the puppies
puppies = realm.where(Dog.class).lessThanOrEqualTo("age", 2).findAll();
puppies.addChangeListener(puppiesListener);
dogListener = new RealmChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onChange() {
// ... do something with the updated Dog instance
}};
dog = realm.where(Dog.class).equals("name", "Fido").findFirst();
dog.addChangeListener(dogListener);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
// Remove the listeners
puppies.removeChangeListener(puppiesListener);
dog.removeChangeListener(dogListener);
// Close the realm instance.
realm.close();
}
}
給類添加Listeners
Person person = realm.where(Person.class).findFirst();
person.getDogs(); // => 2 - Assume there are 2 dogs in the list
person.addChangeListener(new RealmChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onChange() {
// React to the change in the Person instance.
// This will also get called when any referenced dogs are updated.
}
});
Dog dog = person.getDogs().get(0);
realm.beginTransaction();
dog.setAge(5);
realm.commitTransaction();
// Person change listener is called on the next iteration of the run loop because
// a referenced dog object changed.
數據遷移,版本迭代時,數據庫常用
class Person: Object {
dynamic var firstName = ""
dynamic var lastName = ""
dynamic var age = 0
}
在某個版本更新中,變成了下邊這樣
class Person: Object {
dynamic var fullName = ""
dynamic var age = 0
}
那麼就需要用到數據遷移了.
需要考慮跨版本的數據庫遷移,例如v0直接升級到v3版本,而不是只考慮v2升級到v3.
// Example migration adding a new class
RealmMigration migration = new RealmMigration() {
@Override
public void migrate(DynamicRealm realm, long oldVersion, long newVersion) {
// During a migration, a DynamicRealm is exposed. A DynamicRealm is an untyped variant of a normal Realm, but
// with the same object creation and query capabilities.
// A DynamicRealm uses Strings instead of Class references because the Classes might not even exist or have been
// renamed.
// Access the Realm schema in order to create, modify or delete classes and their fields.
RealmSchema schema = realm.getSchema();
/************************************************
// Version 0
class Person
@Required
String firstName;
@Required
String lastName;
int age;
// Version 1
class Person
@Required
String fullName; // combine firstName and lastName into single field.
int age;
************************************************/
// Migrate from version 0 to version 1
if (oldVersion == 0) {
RealmObjectSchema personSchema = schema.get("Person");
// Combine 'firstName' and 'lastName' in a new field called 'fullName'
personSchema
.addField("fullName", String.class, FieldAttribute.REQUIRED)
.transform(new RealmObjectSchema.Function() {
@Override
public void apply(DynamicRealmObject obj) {
obj.set("fullName", obj.getString("firstName") + " " + obj.getString("lastName"));
}
})
.removeField("firstName")
.removeField("lastName");
oldVersion++;
}
/************************************************
// Version 2
class Pet // add a new model class
@Required
String name;
@Required
String type;
class Person
@Required
String fullName;
int age;
RealmList pets; // add an array property
************************************************/
// Migrate from version 1 to version 2
if (oldVersion == 1) {
// Create a new class
RealmObjectSchema petSchema = schema.create("Pet")
.addField("name", String.class, FieldAttribute.REQUIRED)
.addField("type", String.class, FieldAttribute.REQUIRED);
// Add a new field to an old class and populate it with initial data
schema.get("Person")
.addRealmListField("pets", petSchema)
.transform(new RealmObjectSchema.Function() {
@Override
public void apply(DynamicRealmObject obj) {
if (obj.getString("fullName").equals("JP McDonald")) {
DynamicRealmObject pet = realm.createObject("Pet");
pet.setString("name", "Jimbo");
pet.setString("type", "dog");
obj.getList("pets").add(pet);
}
}
});
oldVersion++;
}
/************************************************
// Version 3
class Pet
@Required
String name;
int type; // type becomes int
class Person
String fullName; // fullName is nullable now
RealmList pets; // age and pets re-ordered (no action needed)
int age;
************************************************/
// Migrate from version 2 to version 3
if (oldVersion == 2) {
RealmObjectSchema personSchema = schema.get("Person");
personSchema.setNullable("fullName", true); // fullName is nullable now.
// Change type from String to int
schema.get("Pet")
.addField("type_tmp", int.class)
.transform(new RealmObjectSchema.Function() {
@Override
public void apply(DynamicRealmObject obj) {
String oldType = obj.getString("type");
if (oldType.equals("dog")) {
obj.setLong("type_tmp", 1);
} else if (oldType.equals("cat")) {
obj.setInt("type_tmp", 2);
} else if (oldType.equals("hamster")) {
obj.setInt("type_tmp", 3);
}
}
})
.removeField("type")
.renameField("type_tmp", "type");
oldVersion++;
}
}
Realm的加密方式為:key為64字節,AES-256
加密過的 Realm 只會帶來很少的額外資源占用(通常最多只會比平常慢10%)
注:如果數據庫加密後,由於不知道加密方式,即使有原始key,也無法獲取解密key,所以無法用Realm Browser查看.
注:如果數據庫加密,每次獲取Realm實例時,必須使用encryptionKey.
byte[] key = new byte[64];
new SecureRandom().nextBytes(key);
RealmConfiguration config = new RealmConfiguration.Builder(context)
.encryptionKey(key)
.build();
Realm realm = Realm.getInstance(config);
GSON is a library created by Google for deserializing and serializing JSON. When using Realm with GSON 2.3.1 (latest version), you have to specify an ExclusionStrategy.
// Using the User class
public class User extends RealmObject {
private String name;
private String email;
// getters and setters left out ...
}
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder()
.setExclusionStrategies(new ExclusionStrategy() {
@Override
public boolean shouldSkipField(FieldAttributes f) {
return f.getDeclaringClass().equals(RealmObject.class);
}
@Override
public boolean shouldSkipClass(Class clazz) {
return false;
}
})
.create();
String json = "{ name : 'John', email : 'john@corporation.com' }";
User user = gson.fromJson(json, User.class);
uses GSON internally, it also needs a properly configured GsonConverter if you want to deserialize network JSON data to RealmObjects.
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder()
.setExclusionStrategies(new ExclusionStrategy() {
@Override
public boolean shouldSkipField(FieldAttributes f) {
return f.getDeclaringClass().equals(RealmObject.class);
}
@Override
public boolean shouldSkipClass(Class clazz) {
return false;
}
})
.create();
// Configure Retrofit to use the proper GSON converter
RestAdapter restAdapter = new RestAdapter.Builder()
.setEndpoint("https://api.github.com")
.setConverter(new GsonConverter(gson))
.build();
GitHubService service = restAdapter.create(GitHubService.class);
With Retrofit 2, GSON is no longer used by default, but can be used via its converter module.
dependencies {
compile 'com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.0.0-beta3'
compile 'com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.0.0-beta3'
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder()
.setExclusionStrategies(new ExclusionStrategy() {
@Override
public boolean shouldSkipField(FieldAttributes f) {
return f.getDeclaringClass().equals(RealmObject.class);
}
@Override
public boolean shouldSkipClass(Class clazz) {
return false;
}
})
.create();
Retrofit retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl("https://api.github.com")
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create(gson)
.build();