大學研究了三年的.Net,由於偶然的機會,拿到IBM的Java web實習offer,所以決定轉行搞Java(綜合了校招情況、發展前景和其他各種因素)。
下面是我在學習Java web的一些學習筆記(可能會比較亂,希望能做個備忘,如果能對您有幫助那就更好了)
1.Servlet的生命周期:
Servlet生命周期分為三個階段:
1,初始化階段:調用init()方法
2,響應客戶請求階段:調用service()方法
Service()方法內部對請求的類型(get/post)進行了判斷,自動調用doPost/doGet
3,終止階段:調用destroy()方法
2.Servlet的單例多線程:
單例:Servlet只在用戶第一次請求時被實例化,並且是單例的,在服務器重啟或關閉時才會被銷毀。
多線程:當請求到達時,Servlet容器(Tomcat...)通過線程池中可用的線程給請求者並執行Service方法。
1.多線程
線程創建的兩種方法:
第一種,實現Runnable接口

package test.Thread;
import org.junit.Test;
//This example shows the two method to create new thread.The java file "MyThread" shows the other method.
public class NewThread{
@Test
public void Fun(){
RunnableThread rt = new RunnableThread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(rt,"First");
Thread t2 = new Thread(rt,"Second");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
class RunnableThread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
}

第二種,繼承Thread類

package test.Thread;
public class MyThread extends Thread{
//The constructor without parameter
public MyThread(){
}
//The constructor with name parameter
public MyThread(String name){
super(name);
}
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
System.out.println(this.getName());
}
}
}

線程的同步
使用同步鎖synchronized,參見賣票程序。同步的對象必須是同一個對象。

package test.Thread;
import org.junit.Test;
public class Thread_Synchronized {
public static void main(String[] args){
SynchronizedRunnableThread srt = new SynchronizedRunnableThread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(srt,"window1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(srt,"window2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(srt,"window3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
class SynchronizedRunnableThread implements Runnable{
private static int tickets=100;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
//We can use the definition of class,because it's unique
/*
synchronized(this){
if(tickets>0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" is selling the "+(tickets--)+"th ticket");
}
}
*/
//or we can use the other method--synchronized method
sellTickets();
}
}
private synchronized void sellTickets() {
if(tickets>0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" is selling the "+(tickets--)+"th ticket");
}
}
}

2.IO流
四大流:
InputStream、OutputStream 用於任意對象(二進制格式)
Writer、Reader 用於字符對象(字符格式)
使用示例:

package test.Stream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
public class FileInputStream_FileOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//The difference of "FileInputStream" and "FileReader" is that "FileInputStream" read the file with byte,
//but "FileReader" read with Unicode,in other words,"FileReader" can read Chinese word.
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream("D:\\read.txt");
FileOutputStream os =new FileOutputStream("D:\\FileOutputStream.txt");
int ch = is.read();
while(ch!=-1){
os.write(ch);
System.out.print((char)ch);
ch = is.read();
}
os.flush();
os.close();
is.close();
}
}


package test.Stream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
public class FileReader_FileWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
FileReader fr = new FileReader("D:\\read.txt");
FileWriter fw =new FileWriter("D:\\write.txt");
int ch = fr.read();
while(ch!=-1){
fw.write(ch);
ch = fr.read();
}
fw.flush();
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
}

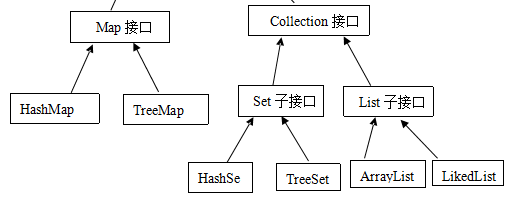
3.集合類
1.jsp工作原理:
當一個JSP文件第一次被請求的時候,Tomcat首先會把這個JSP文件轉換成一個Java源文件。在轉換過程中如果發現JSP文件有語法錯誤,轉換過程將中斷,並向服務端和客戶端輸出出錯信息。如果轉換成功,Tomcat用javac把該Java源文件編譯成相應的.class文件並將該.class文件加載到內存中。(通過查看原文件,可知jsp最終也是轉化被成Servlet,.java就是一個Servlet)
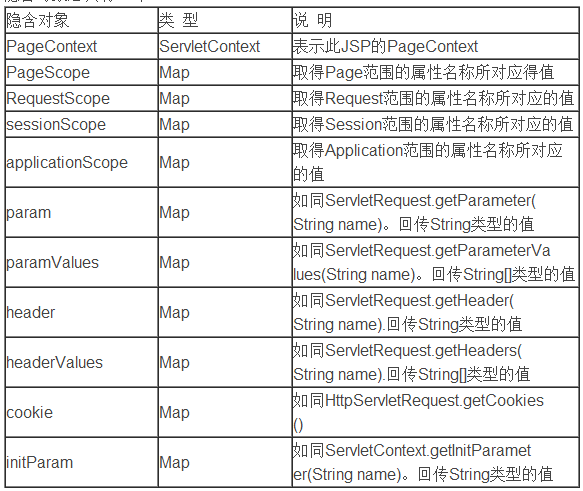
2.jsp九大內置對象?
request 用戶端請求,此請求會包含來自GET/POST請求的參數
response 網頁傳回用戶端的回應
pageContext 網頁的屬性
session 與請求有關的會話信息
application
out 用來傳送回應的輸出
config 存取servlet實例的初始化參數
page
exception
3.JSTL標簽
1.表達式控制標簽:out、set、remove、catch
2.流程控制標簽:if、choose、when、otherwise
3.循環標簽:forEach、forTokens
4.URL操作標簽:import、url、redirect
4.EL表達式