在前面一篇文章中已經講述了在進程和線程的由來,今天就來講一下在Java中如何創建線程,讓線程去執行一個子任務。下面先講述一下Java中的應用程序和進程相關的概念知識,然後再闡述如何創建線程以及如何創建進程。下面是本文的目錄大綱:
一.Java中關於應用程序和進程相關的概念
二.Java中如何創建線程
三.Java中如何創建進程
一.Java中關於應用程序和進程相關的概念
在Java中,一個應用程序對應著一個JVM實例(也有地方稱為JVM進程),一般來說名字默認為java.exe或者javaw.exe(windows下可以通過任務管理器查看)。Java采用的是單線程編程模型,即在我們自己的程序中如果沒有主動創建線程的話,只會創建一個線程,通常稱為主線程。但是要注意,雖然只有一個線程來執行任務,不代表JVM中只有一個線程,JVM實例在創建的時候,同時會創建很多其他的線程(比如垃圾收集器線程)。
由於Java采用的是單線程編程模型,因此在進行UI編程時要注意將耗時的操作放在子線程中進行,以避免阻塞主線程(在UI編程時,主線程即UI線程,用來處理用戶的交互事件)。
二.Java中如何創建線程
在java中如果要創建線程的話,一般有兩種方式:1)繼承Thread類;2)實現Runnable接口。
1.繼承Thread類
繼承Thread類的話,必須重寫run方法,在run方法中定義需要執行的任務。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12class MyThread extends Thread{
private static int num = 0;
public MyThread(){
num++;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("主動創建的第"+num+"個線程");
}
}
創建好了自己的線程類之後,就可以創建線程對象了,然後通過start()方法去啟動線程。注意,不是調用run()方法啟動線程,run方法中只是定義需要執行的任務,如果調用run方法,即相當於在主線程中執行run方法,跟普通的方法調用沒有任何區別,此時並不會創建一個新的線程來執行定義的任務。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread{
private static int num = 0;
public MyThread(){
num++;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("主動創建的第"+num+"個線程");
}
}
在上面代碼中,通過調用start()方法,就會創建一個新的線程了。為了分清start()方法調用和run()方法調用的區別,請看下面一個例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("主線程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId());
MyThread thread1 = new MyThread("thread1");
thread1.start();
MyThread thread2 = new MyThread("thread2");
thread2.run();
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread{
private String name;
public MyThread(String name){
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("name:"+name+" 子線程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
}
運行結果:
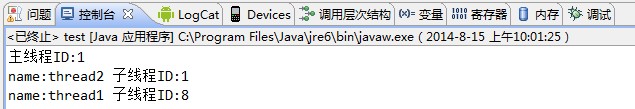
從輸出結果可以得出以下結論:
1)thread1和thread2的線程ID不同,thread2和主線程ID相同,說明通過run方法調用並不會創建新的線程,而是在主線程中直接運行run方法,跟普通的方法調用沒有任何區別;
2)雖然thread1的start方法調用在thread2的run方法前面調用,但是先輸出的是thread2的run方法調用的相關信息,說明新線程創建的過程不會阻塞主線程的後續執行。
2.實現Runnable接口
在Java中創建線程除了繼承Thread類之外,還可以通過實現Runnable接口來實現類似的功能。實現Runnable接口必須重寫其run方法。
下面是一個例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("主線程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId());
MyRunnable runnable = new MyRunnable();
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.start();
}
}
class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
public MyRunnable() {
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("子線程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
}
Runnable的中文意思是“任務”,顧名思義,通過實現Runnable接口,我們定義了一個子任務,然後將子任務交由Thread去執行。注意,這種方式必須將Runnable作為Thread類的參數,然後通過Thread的start方法來創建一個新線程來執行該子任務。如果調用Runnable的run方法的話,是不會創建新線程的,這根普通的方法調用沒有任何區別。
事實上,查看Thread類的實現源代碼會發現Thread類是實現了Runnable接口的。
在Java中,這2種方式都可以用來創建線程去執行子任務,具體選擇哪一種方式要看自己的需求。直接繼承Thread類的話,可能比實現Runnable接口看起來更加簡潔,但是由於Java只允許單繼承,所以如果自定義類需要繼承其他類,則只能選擇實現Runnable接口。
三.Java中如何創建進程
在Java中,可以通過兩種方式來創建進程,總共涉及到5個主要的類。
第一種方式是通過Runtime.exec()方法來創建一個進程,第二種方法是通過ProcessBuilder的start方法來創建進程。下面就來講一講這2種方式的區別和聯系。
首先要講的是Process類,Process類是一個抽象類,在它裡面主要有幾個抽象的方法,這個可以通過查看Process類的源代碼得知:
位於java.lang.Process路徑下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15public abstract class Process
{
abstract public OutputStream getOutputStream(); //獲取進程的輸出流
abstract public InputStream getInputStream(); //獲取進程的輸入流
abstract public InputStream getErrorStream(); //獲取進程的錯誤流
abstract public int waitFor() throws InterruptedException; //讓進程等待
abstract public int exitValue(); //獲取進程的退出標志
abstract public void destroy(); //摧毀進程
}
1)通過ProcessBuilder創建進程
ProcessBuilder是一個final類,它有兩個構造器:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20public final class ProcessBuilder
{
private List<String> command;
private File directory;
private Map<String,String> environment;
private boolean redirectErrorStream;
public ProcessBuilder(List<String> command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.command = command;
}
public ProcessBuilder(String... command) {
this.command = new ArrayList<String>(command.length);
for (String arg : command)
this.command.add(arg);
}
....
}
構造器中傳遞的是需要創建的進程的命令參數,第一個構造器是將命令參數放進List當中傳進去,第二構造器是以不定長字符串的形式傳進去。
那麼我們接著往下看,前面提到是通過ProcessBuilder的start方法來創建一個新進程的,我們看一下start方法中具體做了哪些事情。下面是start方法的具體實現源代碼:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31public Process start() throws IOException {
// Must convert to array first -- a malicious user-supplied
// list might try to circumvent the security check.
String[] cmdarray = command.toArray(new String[command.size()]);
for (String arg : cmdarray)
if (arg == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// Throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if command is empty
String prog = cmdarray[0];
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null)
security.checkExec(prog);
String dir = directory == null ? null : directory.toString();
try {
return ProcessImpl.start(cmdarray,
environment,
dir,
redirectErrorStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
// It's much easier for us to create a high-quality error
// message than the low-level C code which found the problem.
throw new IOException(
"Cannot run program \"" + prog + "\""
+ (dir == null ? "" : " (in directory \"" + dir + "\")")
+ ": " + e.getMessage(),
e);
}
}
該方法返回一個Process對象,該方法的前面部分相當於是根據命令參數以及設置的工作目錄進行一些參數設定,最重要的是try語句塊裡面的一句:
1 2 3 4return ProcessImpl.start(cmdarray,
environment,
dir,
redirectErrorStream);
說明真正創建進程的是這一句,注意調用的是ProcessImpl類的start方法,此處可以知道start必然是一個靜態方法。那麼ProcessImpl又是什麼類呢?該類同樣位於java.lang.ProcessImpl路徑下,看一下該類的具體實現:
ProcessImpl也是一個final類,它繼承了Process類:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14final class ProcessImpl extends Process {
// System-dependent portion of ProcessBuilder.start()
static Process start(String cmdarray[],
java.util.Map<String,String> environment,
String dir,
boolean redirectErrorStream)
throws IOException
{
String envblock = ProcessEnvironment.toEnvironmentBlock(environment);
return new ProcessImpl(cmdarray, envblock, dir, redirectErrorStream);
}
....
}
這是ProcessImpl類的start方法的具體實現,而事實上start方法中是通過這句來創建一個ProcessImpl對象的:
1return new ProcessImpl(cmdarray, envblock, dir, redirectErrorStream);
而在ProcessImpl中對Process類中的幾個抽象方法進行了具體實現。
說明事實上通過ProcessBuilder的start方法創建的是一個ProcessImpl對象。
下面看一下具體使用ProcessBuilder創建進程的例子,比如我要通過ProcessBuilder來啟動一個進程打開cmd,並獲取ip地址信息,那麼可以這麼寫:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ProcessBuilder pb = new ProcessBuilder("cmd","/c","ipconfig/all");
Process process = pb.start();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(process.getInputStream());
while(scanner.hasNextLine()){
System.out.println(scanner.nextLine());
}
scanner.close();
}
}
第一步是最關鍵的,就是將命令字符串傳給ProcessBuilder的構造器,一般來說,是把字符串中的每個獨立的命令作為一個單獨的參數,不過也可以按照順序放入List中傳進去。
至於其他很多具體的用法不在此進行贅述,比如通過ProcessBuilder的environment方法和directory(File directory)設置進程的環境變量以及工作目錄等,感興趣的朋友可以查看相關API文檔。
2)通過Runtime的exec方法來創建進程
首先還是來看一下Runtime類和exec方法的具體實現,Runtime,顧名思義,即運行時,表示當前進程所在的虛擬機實例。
由於任何進程只會運行於一個虛擬機實例當中,所以在Runtime中采用了單例模式,即只會產生一個虛擬機實例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19public class Runtime {
private static Runtime currentRuntime = new Runtime();
/**
* Returns the runtime object associated with the current Java application.
* Most of the methods of class <code>Runtime</code> are instance
* methods and must be invoked with respect to the current runtime object.
*
* @return the <code>Runtime</code> object associated with the current
* Java application.
*/
public static Runtime getRuntime() {
return currentRuntime;
}
/** Don't let anyone else instantiate this class */
private Runtime() {}
...
}
從這裡可以看出,由於Runtime類的構造器是private的,所以只有通過getRuntime去獲取Runtime的實例。接下來著重看一下exec方法 實現,在Runtime中有多個exec的不同重載實現,但真正最後執行的是這個版本的exec方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7public Process exec(String[] cmdarray, String[] envp, File dir)
throws IOException {
return new ProcessBuilder(cmdarray)
.environment(envp)
.directory(dir)
.start();
}
可以發現,事實上通過Runtime類的exec創建進程的話,最終還是通過ProcessBuilder類的start方法來創建的。
下面看一個例子,看一下通過Runtime的exec如何創建進程,還是前面的例子,調用cmd,獲取ip地址信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String cmd = "cmd "+"/c "+"ipconfig/all";
Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(process.getInputStream());
while(scanner.hasNextLine()){
System.out.println(scanner.nextLine());
}
scanner.close();
}
}
要注意的是,exec方法不支持不定長參數(ProcessBuilder是支持不定長參數的),所以必須先把命令參數拼接好再傳進去。
關於在Java中如何創建線程和進程的話,暫時就講這麼多了,感興趣的朋友可以參考相關資料、
參考資料:
http://luckykapok918.blog.163.com/blog/static/205865043201210272168556/
http://www.cnblogs.com/ChrisWang/archive/2009/12/02/use-java-lang-process-and-processbuilder-to-create-native-application-process.html
http://lavasoft.blog.51cto.com/62575/15662/
問啊-一鍵呼叫程序員答題神器,牛人一對一服務,開發者編程必備官方網站:www.wenaaa.com
QQ群290551701 聚集很多互聯網精英,技術總監,架構師,項目經理!開源技術研究,歡迎業內人士,大牛及新手有志於從事IT行業人員進入!