JSP是J2EE標准之一,和ASP.NET中的aspx作用和開發類似,這篇博客我們通過一個簡單的實例,看一下JSP的部署、執行原理及生命周期等。
新建
我們新建一個項目,按照Tomcat要求的基本文檔結構,名為MyFirstJSP,在這個項目下新建一個JSP,名為HelloWorld.jsp,目的只是輸出一行HelloWorld:
[html]
<html>
<head>
<title>login</title>
</head>
<body>
<% out.println("HelloWorld"); %>
</body>
<html>
<html>
<head>
<title>login</title>
</head>
<body>
<% out.println("HelloWorld"); %>
</body>
<html>
部署
JSP的部署,不像Servlet一樣繁瑣(可以參見博客博客《Tomcat下Servlet登錄實例》),不需要修改配置文件,也不需要指定jsp的動作指向,按照上面的步驟新建完畢項目以後,打開Tomcat,輸入
配置文件
打開Tomcat根目錄下conf下的web.xml,可以發現以下配置:
[html]
<!-- The mapping for the JSP servlet -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>jsp</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.jsp</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>jsp</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.jspx</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!-- The mapping for the JSP servlet -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>jsp</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.jsp</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>jsp</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.jspx</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
現在我們把配置文件中的*.jspx修改為*.test,把我們的HelloWorld.jsp修改為HelloWorld.test,然後訪問http://localhost:8080/MyFirstJSP/HelloWorld.test,執行結果為:
和上面相同,其實這個配置的意思是:把什麼樣的文件當做jsp來解析,此處也可以修改為其它格式。
可見,如果配置合理,拓展名對jsp執行無影響,那麼jsp的執行原理是什麼?我們繼續看這個配置文件,可以發現如下配置:
[html]
<servlet>
<servlet-name>jsp</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>fork</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>xpoweredBy</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>3</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>jsp</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>fork</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>xpoweredBy</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>3</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
可見,此配置的作用是找到處理jsp的類,經過比對代碼,其實就是把jsp當做Servlet處理,當然只憑這個說服力不大,我們繼續往下看。
進入D:\Program Files (x86)\apache-tomcat-6.0.33\work\Catalina\localhost\MyFirstJSP\org\apache\jsp下,發現如下的文檔結構:
在此處會自動生成與之對應的java文件和類文件,因為剛才我們嘗試了test的文件,所以此處也生成了對應的test的java和類文件。我們打開HelloWorld_jsp.java,找到主要的函數_jspService:
[java]
<SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: SimSun">public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, ServletException {
PageContext pageContext = null;
HttpSession session = null;
ServletContext application = null;
ServletConfig config = null;
JspWriter out = null;
Object page = this;
JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;
try {
response.setContentType("text/html");
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
out.write("<html>\r\n");
out.write("\t<head>\r\n");
out.write("\t\t<title>login</title>\r\n");
out.write("\t</head>\r\n");
out.write("\t<body>\r\n");
out.write("\t\t\t");
out.println("HelloWorld");
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("\t</body>\r\n");
out.write("<html>");
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (!(t instanceof SkipPageException)){
out = _jspx_out;
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)
try { out.clearBuffer(); } catch (java.io.IOException e) {}
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);
}
} finally {
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);
}
}</SPAN>
public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, ServletException {
PageContext pageContext = null;
HttpSession session = null;
ServletContext application = null;
ServletConfig config = null;
JspWriter out = null;
Object page = this;
JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;
try {
response.setContentType("text/html");
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
out.write("<html>\r\n");
out.write("\t<head>\r\n");
out.write("\t\t<title>login</title>\r\n");
out.write("\t</head>\r\n");
out.write("\t<body>\r\n");
out.write("\t\t\t");
out.println("HelloWorld");
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("\t</body>\r\n");
out.write("<html>");
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (!(t instanceof SkipPageException)){
out = _jspx_out;
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)
try { out.clearBuffer(); } catch (java.io.IOException e) {}
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);
}
} finally {
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);
}
} 發現什麼沒有?這個函數的參數為HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse,可能的異常為ServletException;可見此處是把jsp當做了Servlet處理。
生命周期
jsp第一次加載會編譯,所以比較慢,編譯以後訪問即不再變化(jsp文件不變前提),可以使用工具諸如Weblogic jspc對jsp進行預編譯。
為了方便說明,我們找到Tomcat源文件HttpJspBase.java,打開這個文件,函數如下(省略本文章不需要的代碼):[java] view plaincopyprint?
public abstract class HttpJspBase
extends HttpServlet
implements HttpJspPage
{
public final void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
_jspService(request, response);
}
public abstract void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException;
}
public abstract class HttpJspBase
extends HttpServlet
implements HttpJspPage
{
public final void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
_jspService(request, response);
}
public abstract void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException;
} 根據源碼和簡單解釋一下這個過程:
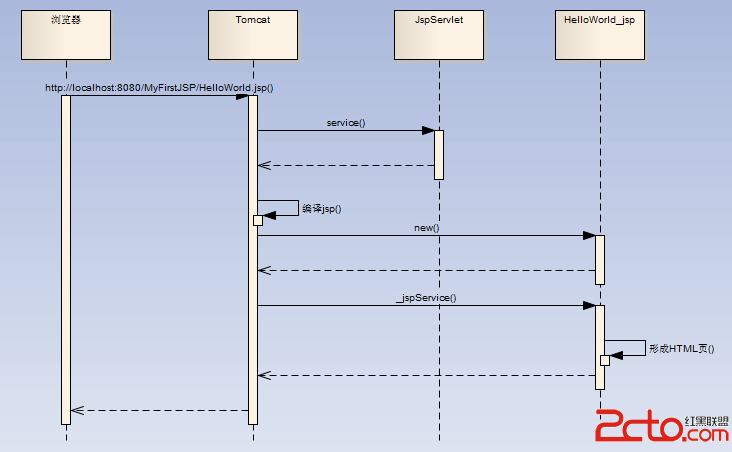
客戶端首先發出請求,Tomcat接收到請求
如上面配置文件所示,執行JspServlet的service()函數
如果jsp第一次被請求,則編譯jsp為Servlet
因為Helloworld_jsp已經被編譯為Servlet,以後的執行順序和普通的Servlet一樣先執行new()
再執行_jspService()
形成html,返回給浏覽器
總結
既然jsp被編譯後就是一個Servlet,為什麼還要有jsp?jsp的出現在Servlet之後,目的就是簡化Servlet的開發和部署。