從本篇開始,將進一步去分析各組件的實現細節,深入CI核心的黑盒內部(研究之後,其實就應該是白盒了,僅僅對於應用來說,它應該算是黑盒),從而更好的去認識、把握這個框架。
按照慣例,在開始之前,我們貼上CI中不完全的核心組件圖:
由於BenchMark是CI中第一個加載的cZ喎?http://www.Bkjia.com/kf/ware/vc/" target="_blank" class="keylink">vcmXX6bz+o6zS8rTLztLDx7XEt9bO9srXz8i007jD1+m8/r+qyryho0JlbmNoTWFya7XEuqzS5bfHs6PD98i3o6zKudPDuf1CZW5jaE1hcmu5pL7ftcTNrNGn06a4w7HIvc/H5bP+o6zV4srH0ru49rv517zX6bz+oaO8yMi7ysdCZW5jaE1hcmujrM7Sw8ex47/JtPO1qLLCz+ujrEJN1+m8/rXE1vfSqrmmxNy+zcrHvMfCvLPM0PK1xNTL0NDKsbzkoaLE2rTmyrnTw6GiY3B1yrnTw7XIx+m/9qGjPC9wPgo8cD7PyL+0wODNvDo8L3A+CjxwPjxpbWcgc3JjPQ=="http://www.2cto.com/uploadfile/Collfiles/20141107/20141107084017230.jpg" alt="\">
這個組件結構較簡單,只有一個marker內部變量和三個對外的接口:
1 Elapsed_time 2 Mark 3 Memory_usage
下面一個個展開來看:
函數的簽名為:
function mark($name)
這個函數接受一個string類型的參數,而實現更簡單,只有一句話:
$this->marker[$name] = microtime();
也就是說這個函數只是用於記錄函數調用時刻的時間點。
值得注意的是,由於Controller中的特殊處理(之後我們會詳細解釋),你的應用程序控制器中可以使用$this->benchmark->mark($name);的方式來添加運行的時間點,例如:
$this->benchmark->mark("function_test_start");
$this->_test();
$this->benchmark->mark("function_test_end");
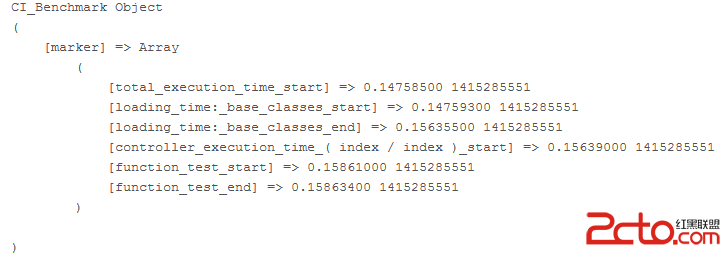
print_r($this->benchmark);
其中,function_test_start和function_test_end分別用於記錄函數調用開始和結束的時間點
打印出的結果:
現在要計算函數的調用時間,需要用到BenchMark組件的第二個函數elapsed_time
函數的簽名為:
function elapsed_time($point1 = '', $point2 = '', $decimals = 4)
3個參數均為可選參數
(1). 如果$point1 為空,則返回’{elapsed_time}’
if ($point1 == '') {
return '{elapsed_time}';
}
納尼!明明應該返回的是時間,怎麼反而返回的是字符串,而且這麼奇怪(類似smarty的標簽)。其實,在Output組件中,{elapsed_time}會被替換,我們暫時看一下替換的方式:
$elapsed = $BM->elapsed_time('total_execution_time_start', 'total_execution_time_end');
$output = str_replace('{elapsed_time}', $elapsed, $output);
也就是說,沒有指定參數的情況下,調用該函數實際得到的是total_execution_time_start這個時間點到total_execution_time_end這個時間點的時間差。更進一步,由於total_execution_time_start是在BM加載之後設置的第一個mark點(total_execution_time_end並未定義,返回的是當前時間點),該函數返回的實際就是系統的加載和運行時間。
(2).如果調用的是未知的mark點。則結果是未知的,直接返回空:
if ( ! isset($this->marker[$point1]))
{
return '';
}
(3).如果沒有設置$point2的mark點,則將$point2的mark點設置為當前的時間點。
if ( ! isset($this->marker[$point2]))
{
$this->marker[$point2] = microtime();
}
(4).最後返回的兩個mark點的時間差:
list($sm, $ss) = explode(' ', $this->marker[$point1]);
list($em, $es) = explode(' ', $this->marker[$point2]);
return number_format(($em + $es) - ($sm + $ss), $decimals);
還看之前的例子,這裡我們可以通過調用:
echo $this->benchmark->elapsed_time("function_test_start","function_test_end");
得到函數的執行時間.
這個函數返回的是系統的內存使用情況(MB單位),與{elapsed_time} 一樣,這個函數返回的{memory_usage}也會在Output中被替換:
$memory = ( ! function_exists('memory_get_usage')) ? '0' : round(memory_get_usage()/1024/1024, 2).'MB';
$output = str_replace('{memory_usage}', $memory, $output);
由於BenchMark組件本身較簡單,我們不做更多的解釋。
最後,貼上這個組件的源碼:

marker[$name] = microtime();
}
/**
* Calculates the time difference between two marked points.
* If the first parameter is empty this function instead returns the {elapsed_time} pseudo-variable. This permits the full system
* @access public
* @param string a particular marked point
* @param string a particular marked point
* @param integer the number of decimal places
* @return mixed
*/
function elapsed_time($point1 = '', $point2 = '', $decimals = 4)
{
if ($point1 == '')
{
return '{elapsed_time}';
}
if ( ! isset($this->marker[$point1]))
{
return '';
}
if ( ! isset($this->marker[$point2]))
{
$this->marker[$point2] = microtime();
}
list($sm, $ss) = explode(' ', $this->marker[$point1]);
list($em, $es) = explode(' ', $this->marker[$point2]);
return number_format(($em + $es) - ($sm + $ss), $decimals);
}
/**
* Memory Usage
* This function returns the {memory_usage} pseudo-variable.
*/
function memory_usage()
{
return '{memory_usage}';
}
}