上一篇分析Symfony2框架源碼,探究Symfony2如何完成一個請求的前半部分,前半部分可以理解為Symfony2框架為處理請求做准備工作,包括container生成、緩存、bundls初始化等一些列准備工作(Symfony2源碼分析——啟動過程1)。而這一篇講的是Symfony2如何根據請求的數據生成Response對象,向客戶端返回響應數據。
在分析前需要了解Symfony2的事件驅動機制:Symfony2事件驅動。
言歸正傳,Symfony2請求的工作流程其實是Symfony2內核的事件驅動完成的,下面是Symfony2框架定義好的內核事件:
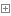
我們可以編寫事件監聽器,監聽相應的內核事件,在Symfony2觸發該事件的時候,相應的事件監聽器就會執行。監聽和喚醒形象的描述,就像,你(事件監聽器)參加校運會,去大會(Symfony2)登記(監聽)參加50米短跑(事件),當50米短跑比賽開始了(事件被觸發),那你就奔跑吧(監聽器執行,其實就是一個執行函數,函數完成什麼工作就取決於你的需求了),少年。
Symfony2的內核事件處理流程大部分工作都在HttpKernel::handleRaw方法中:
1 private function handleRaw(Request $request, $type = self::MASTER_REQUEST)
2 {
3 $this->requestStack->push($request);
4
5 // request
6 // 初始化事件,事件對象會被傳遞給監聽器,所以事件可以說是一個信息的載體,事件內存放著監聽器感興趣的數據。
7 $event = new GetResponseEvent($this, $request, $type);
8 // 觸發kernel.request事件,後續詳細講解EventDispatcher::dispatch方法的實現,
9 // 這裡我們需要知道的是,dispatcher把$event傳遞給所有監聽了kernel.request事件的監聽器,監聽器將會執行。
10 // kernel.request事件發生在controller執行之前,我們可以在這一步奏完成路由解析等為controller執行提供准備數據,
11 // 在這個過程允許我們直接生成Response對象,向客戶端輸出數據,那麼controller就不會被執行了。
12 $this->dispatcher->dispatch(KernelEvents::REQUEST, $event);
13
14 // 如果我們在kernel.request事件生成了Response對象(響應數據),那麼就跳過kernel.controller、kernel.view事件、
15 // controller也會被跳過,直接執行kernel.response事件。
16 if ($event->hasResponse()) {
17 return $this->filterResponse($event->getResponse(), $request, $type);
18 }
19
20 // load controller
21 // 根據路由規則返回 一個對象或者數組或者字符串 ,如果$controller是一個數組,$controller[0]是存放的是要執行的controller對象,
22 // $controller[0]存放的是controller對象執行的方法,即action,方法的參數沒有保存在$controller數組中;
23 // 如果$controller是對象,那麼該對象就實現了__invoke 方法;
24 // 如果$controller是字符串,那麼$controller就是要運行的函數的函數名。
25 // 圖2是$controller的一個var_dump例子
26 if (false === $controller = $this->resolver->getController($request)) {
27 throw new NotFoundHttpException(sprintf('Unable to find the controller for path "%s". Maybe you forgot to add the matching route in your routing configuration?', $request->getPathInfo()));
28 }
29
30 $event = new FilterControllerEvent($this, $controller, $request, $type);
31 // 觸發kernel.controller事件,這個事件發生在controller執行前。我們可以通過監聽這個事件在controller執行前修改controller,
32 // 或者完成一些動作。
33 $this->dispatcher->dispatch(KernelEvents::CONTROLLER, $event);
34 $controller = $event->getController();
35
36 // controller arguments
37 // 從request對象中獲取controller方法的參數
38 $arguments = $this->resolver->getArguments($request, $controller);
39
40 // call controller
41 // 執行controller
42 $response = call_user_func_array($controller, $arguments);
43
44 // view
45 // 如果$response不是Response對象,那麼kernel.view事件就會觸發,監聽kernel.view事件的監聽器通過$response值生成Response對象。
46 if (!$response instanceof Response) {
47 $event = new GetResponseForControllerResultEvent($this, $request, $type, $response);
48 $this->dispatcher->dispatch(KernelEvents::VIEW, $event);
49
50 if ($event->hasResponse()) {
51 $response = $event->getResponse();
52 }
53
54 if (!$response instanceof Response) {
55 $msg = sprintf('The controller must return a response (%s given).', $this->varToString($response));
56
57 // the user may have forgotten to return something
58 if (null === $response) {
59 $msg .= ' Did you forget to add a return statement somewhere in your controller?';
60 }
61 throw new \LogicException($msg);
62 }
63 }
64
65 // 觸發kernel.response事件,在向客戶端輸出Response對象前,我們可以對Response對象進行修改,
66 // 例如修改response頭部,設置緩存、壓縮輸出數據等。
67
68 // 接著觸發kernel.finish_request事件,把當前請求從請求棧中彈出,當前請求就完成。
69 return $this->filterResponse($response, $request, $type);
70
71 // 千萬別忘記了,filterResponse執行完後,Symfony2內核事件處理流程還有最後一步,位於app_dev.php[app.php]最後一行,
72 // $kernel->terminate($request, $response);這個方法觸發kernel.terminate事件,此時,Symfony2已經響應了客戶端的請求,
73 // 向客戶端輸出了Response對象。監聽kernel.terminate事件的監聽器,主要是為了完成一些耗時的操作,操作的結果不需要返回給
74 // 客戶端的,例如郵件發送、圖片壓縮等等。
75 // 到這裡,Symfony2的整個流程就走完了。
76 }
HttpKernel::filterResponse方法和HttpKernel::finishRequest方法:


圖2
Symfony2框架的事件分發機制的核心代碼:
1 public function dispatch($eventName, Event $event = null)
2 {
3 if (null === $event) {
4 $event = new Event();
5 }
6
7 $event->setDispatcher($this);
8 $event->setName($eventName);
9
10 if (!isset($this->listeners[$eventName])) {
11 return $event;
12 }
13
14 // $eventName即:KernelEvents::REQUEST、KernelEvents::CONTROLLER、KernelEvents::VIEW、KernelEvents::RESPONSE、KernelEvents::TERMINATE等
15 // getListeners返回所有監聽$eventName事件的監聽器
16 $this->doDispatch($this->getListeners($eventName), $eventName, $event);
17
18 return $event;
19 }
20
21 protected function doDispatch($listeners, $eventName, Event $event)
22 {
23 // 監聽器執行
24 foreach ($listeners as $listener) {
25 call_user_func($listener, $event, $eventName, $this);
26 // 如果其中一個監聽器把$event的propagationStopped屬性設置為true,那麼表示$eventName這一事件終止執行,
27 // 事件不會往$listeners裡尚未執行的監聽器傳遞該事件。
28 if ($event->isPropagationStopped()) {
29 break;
30 }
31 }
32 }
我個人感覺毛德操先生的書linux內核情景分析,分析的很透徹的,對整個Linux內核的講解很不錯.具體到啟動過程,這個啟動過程很泛的,你只需要知道整體的啟動過程,其他的細節,還得看內核源碼講解,所以,推薦你看點博客了解下啟動大體過程,具體到每個細節,看linux內核情景分析吧.
1.這個dialog是由PhoneWindowManager控制的,在PhoneWindowManager的interceptKeyTq方法中,代碼是這一行
mHandler.postDelayed(mPowerLongPress, ViewConfiguration.getGlobalActionKeyTimeout());
mProwerLongPress是一個Runnable,執行時調用GlobalActions中的showDialog方法。所以這個dialog是由GlobalActions管理的,PowerDialog是之前版本中的,現在已經棄用了。
2.可以在GlobalActions中createDialog方法中mSilentModeToggle action的onToggle方法中加入
mAudioManager.setVibrateSetting(AudioManager.VIBRATE_TYPE_RINGER, on ? AudioManager.VIBRATE_SETTING_ON : AudioManager.VIBRATE_SETTING_OFF);
這一句,仿照鈴聲的處理,應該沒問題,不過沒試所以也不能確定。
希望對你有幫助。