1、復制表結構 將表hello的結構復制一份為表hello3
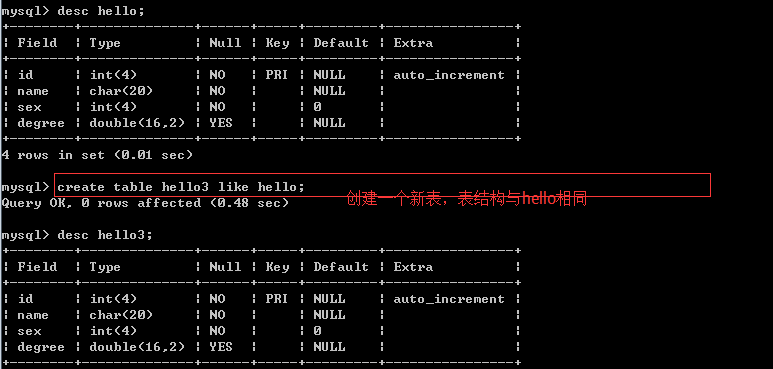
2、復制數據
a、如果兩張表的結構一樣且你要復制所有列的數據
mysql> insert into hello3 select * from hello;
b、兩張表結可能不一樣且你只要復制部分列的數據
mysql> insert into hello3 (name,sex,degree) select name,sex,degree from hello;
1、create 創建索引(只能創建普通索引和唯一索引)
創建普通索引:mysql> create index in_name on hello(name); 給表hello中的name列創建名為 in_name的索引。
創建唯一索引:mysql> create unique index un_name on hello(name); 給表hello中的name列創建唯一索引名為 un_name的索引。
查看索引:mysql> show index from hello; 查看表 hello的索引。
刪除索引:mysql> drop index in_name on hello; 刪除hello表中名為in_name的索引。
2、alter 創建索引(創建索引的通用方式)
創建普通索引:mysql> alter table hello add index in_name(name); 給表hello中的name列創建名為 in_name的索引。
刪除(普通/唯一)索引:mysql> alter table hello drop index in_name; 刪除表hello中名為in_name的普通索引。
刪除自增:mysql> alter table hello modify id int unsigned not null;刪除表hello中 id列(int類型) 的自增特性。
刪除主鍵索引:mysql> alter table hello drop PRIMARY KEY;
創建唯一索引:mysql> alter table hello add unique(name); 給hello表的 name創建唯一索引 索引名是默認的。
創建主鍵索引:mysql> alter table hello add primary key(id); 給hello表的id字段創建主鍵索引。
將主鍵索引設置為自增:mysql> alter table hello modify id int unsigned not null auto_increment;將hello表中的主鍵id列設置為自增。
主表數據的變化,視圖會時時做相應的變化。如果視圖所依賴的表出現錯誤(被刪除)則視圖也會發生錯誤。
創建視圖:mysql> create view v_hello as select * from hello where id >5;
刪除視圖:mysql> drop view v_hello;
查看視圖的創建過程:mysql> show create view v_hello; 查看視圖v_hello 的創建過程。
字符函數
1、CONCAT(str1,str2,....) 字符鏈接函數
mysql> select concat('A','B' );
2、LCASE(str1) 轉為小寫
mysql> select lcase("MYSQL");
3、UCASE(str1) 轉大寫
mysql> select UCASE("Mysql");
4、LENGTH(str) str的長度
mysql> select length('mysql');
5、LTRIM(Str) 去除前段空格
mysql> select LTRIM(' mysql');
6、RTRIM(str) 去除後端空格
mysql> select RTRIM(' mysql ');
7、REPEAT(str,count) 重復count次
mysql> select repeat('mysql',2);
8、REPLACE(str,search_str,replcae_str) 將str中的search_str 替換為replac_str
mysql> select REPLACE('mysql','m','M');
9、SUBSTRING(str,postion,length) 從str的postion開始取length個字符
mysql> select substring('mysql',1,2); 從1開始
10、SPACE(count) 生成count個空格
mysql> select concat(space(3),'mysql');
數學函數
1、BIN(decimal number): 將十進制轉二進制
2、CEILING(number) 向上取整 mysql> select ceiling(10.12); 結果:11
3、FLOOR(number) 向下取整 mysql> select ceiling(10.12); 結果:10
4、MAX(column) 獲取 最大列
5、MIN(column) 獲取最小列
6、SQRT(num) 開平方
7、RAND() 返回0-1之間的隨機數值
日期函數
1、CURDATE() 返回當前日期格式 yyyy-MM-dd
2、CURTIME()返回檔期時間 12:11:56
3、NOW()返回當前時間 2017-05-12 21:12:34
4、UNIX_TIMESTAMP(date) 返回當前date的時間戳
5、FROM_UNIXTIME()返回UNIX時間戳的日期值
6、WEEK(date)返回當前時間date為一年中的第幾周
7、YEAR(data)返回當前時間date的年份
8、DATEDIFF(expr1,expr2) 返回expr1與expr2之間的天數
無變量:
創建預處理語句:mysql> prepare stmt1 from 'select * from hello where id>5';創建一個名為stmt1的預處理語句
執行預處理語句:mysql> execute stmt1;執行stmt1預處理語句
帶變量:
創建帶參數的預處理語句:mysql> prepare stmt1 from 'select * from hello where id>?'
設置變量:mysql> set @i=6;
執行預處理語句:mysql> execute stmt2 using @i;
刪除預處理語句:mysql> drop prepare stmt2; #mysql> DEALLOCATE PREPARE stmt2;
注意:每一次執行完EXECUTE時,養成好習慣,須執行DEALLOCATE PREPARE … 語句,這樣可以釋放執行中使用的所有數據庫資源(如游標)。
不僅如此,如果一個session的預處理語句過多,可能會達到max_prepared_stmt_count的上限值。
mysql默認事務是自動提交的。在做mysql事務處理時請將數據庫或者表的ENGINE 設置為InnoDB
將表的存儲引擎設置為INNODB:mysql> alter table hello engine=innodb;
設置mysql為非自動提交:mysql> set autocommit=0;
產生事務:mysql> delete from hello where id>7;
事務回滾:mysql> rollback;
事務提交:mysql> commit;
關於事務中的還原點:
創建一個事務:mysql> insert into hello (sex,degree,name) values(1,12312.32,'HHH');
對該事務設置還原點:mysql> savepoint p1;
回滾到指定的還原點:mysql> rollback to p1; 此時事務恢復到p1,也就是p1之後的事務p2 ,p3..這些還原點將失效。
回滾到原始的還原點:mysql> rollback;
<!-- 創建存儲過程 hello1()-->
CREATE PROCEDURE hello1()
BEGIN
SET @i=0;
WHILE @i<100 DO
insert INTO hello (sex,degree,name) VALUES(1,@i,CONCAT('name',@i));
SET @i=@i+1;
END WHILE;
end;
<!-- 查看存儲-->
SHOW PROCEDURE STATUS;
<!-- 查看hello1()存儲過程-->
show CREATE PROCEDURE hello1;
<!-- 執行存儲過程-->
CALL hello1;
參考:http://www.cnblogs.com/jalja/p/4635087.html(MySql觸發器)
mysql中我們的主鍵id如果設置為主鍵自增策略,那我們如何清空表,並且恢復自增列id的值。
方式一:使用truncate table tableName; 該方式在清空表的同時恢復auto_increment 的值。
方式二:
1、mysql> delete from hello3; 清空表 (該方式效率較低)
2、mysql> alter table hello3 auto_increment=1; 恢復auto_increment 的起始值為1