MySQL數據庫創建線程的相關操作是本文我們主要要介紹的內容,MySQL數據庫中,為了提高系統效率,減少頻繁創建線程和中止線程的系統消耗,MySQL使用了線程緩沖區的概念,即如果一個連接斷開,則並不銷毀承載其的線程,而是將此線程放入線程緩沖區,並處於掛起狀態,當下一個新的Connection到來時,首先去線程緩沖區去查找是否有空閒的線程,如果有,則使用之,如果沒有則新建線程。
1.線程創建函數
大家知道,Mysql現在是插件式的存儲引擎,只要實現規定的接口,就可實現自己的存儲引擎。故Mysql的線程創建除了出現在主服務器框架外,存儲引擎也可能會進行線程的創建。通過設置斷點,在我調試的版本中,發現了兩個創建線程的函數。
pthread_create:Mysql自用的創建線程函數
os_thread_create:存儲引擎innobase的創建線程的函數
os_thread_create是存儲引擎innobase的線程函數,先擱淺不研究了,重點看下pthread_create,首先看下其源碼。
- int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread_id, pthread_attr_t *attr,
- pthread_handler func, void *param)
- {
- HANDLE hThread;
- struct pthread_map *map;
- DBUG_ENTER("pthread_create");
- if (!(map=malloc(sizeof(*map))))
- DBUG_RETURN(-1);
- map->funcfunc=func; map->paramparam=param;
- pthread_mutex_lock(&THR_LOCK_thread);
- #ifdef __BORLANDC__
- hThread=(HANDLE)_beginthread((void(_USERENTRY *)(void *)) pthread_start,
- attr->dwStackSize ? attr->dwStackSize :
- 65535, (void*) map);
- #else
- hThread=(HANDLE)_beginthread((void( __cdecl *)(void *)) pthread_start, attr->dwStackSize ? attr->dwStackSize : 65535, (void*) map);
- #endif
- DBUG_PRINT("info", ("hThread=%lu",(long) hThread));
- *thread_id=map->pthreadself=hThread;
- pthread_mutex_unlock(&THR_LOCK_thread);
- if (hThread == (HANDLE) -1)
- {
- int error=errno;
- DBUG_PRINT("error",
- ("Can't create thread to handle request (error %d)",error));
- DBUG_RETURN(error ? error : -1);
- }
- VOID(SetThreadPriority(hThread, attr->priority)) ;
- DBUG_RETURN(0);
- }
上面代碼首先構造了一個map結構體,成員分別是函數地址和傳入參數。然後調用操作系統的接口,_beginthread,但是執行函數並不是傳入的函數——func,而是pthread_start,參數為map。繼續跟蹤pthread_start。
- pthread_handler_t pthread_start(void *param)
- {
- pthread_handler
- func=((struct pthread_map *) param)->func
- void *func_param=((struct pthread_map *) param)->param;
- my_thread_init(); /* Will always succeed in windows */
- pthread_mutex_lock(&THR_LOCK_thread); /* Wait for beginthread to return */
- win_pthread_self=((struct pthread_map *) param)->pthreadself;
- pthread_mutex_unlock(&THR_LOCK_thread);
- free((char*) param); /* Free param from create */
- pthread_exit((void*) (*func)(func_param));
- return 0; /* Safety */
- }
可以看出,pthread_start中調用了map的func元素,作為真正執行的函數體。OK,創建線程的函數跟蹤到此!
2.服務器啟動時創建了哪些函數?
通過在兩個創建線程的地方設置斷點,總結了下,在服務器啟動時,創建了如下的線程。
pthread_create創建的線程:
創建線程函數 線程執行函數
create_shutdown_thread
handle_shutdown
start_handle_manager
handle_manager
handle_connections_methods
handle_connections_sockets
innobase的os_thread_create創建的線程:
創建線程函數 線程執行函數
innobase_start_or_create_for_mysql
io_handler_thread4個)
recv_recovery_from_checkpoint_finish
trx_rollback_or_clean_all_without_sess
innobase_start_or_create_for_mysql
srv_lock_timeout_thread
srv_error_monitor_thread
srv_monitor_thread
srv_master_thread
還可以在調試過程中,通過暫停來看此時服務器中的線程,如下圖:
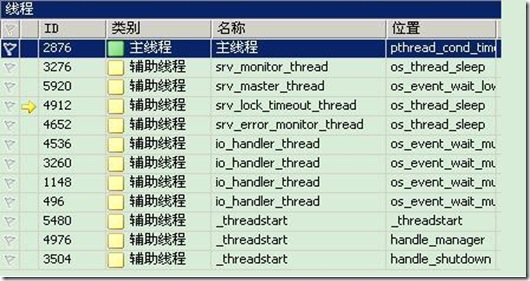
關於MySQL數據庫創建線程的相關知識就介紹到這裡了,希望本次的介紹能夠對您有所收獲!