游標是從數據表中提取出來的數據,以臨時表的形式存放在內存中,在游標中有一個數據指針,在初始狀態下指向的是首記錄,利用fetch語句可以移動該指針,從而對游標中的數據進行各種操作,然後將操作結果寫回數據表中。
定義游標
游標作為一種數據類型,首先必須進行定義,其語法如下。
cursor 游標名 is select 語句;
cursor是定義游標的關鍵詞,select是建立游標的數據表查詢命令。
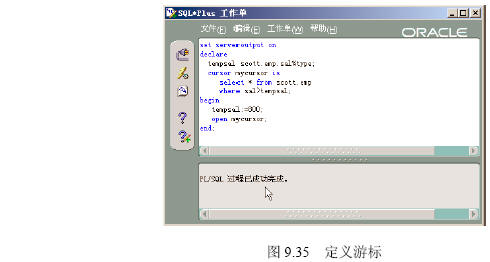
以scott用戶連接數據庫,在【SQLPlus Worksheet】中執行下列PL/SQL程序,該程序定義tempsal為與scott.emps數據表中的sal字段類型相同的變量,mycursor為從scott.emp數據表中提取的sal大於tempsal的數據構成的游標。
執行結果如圖9.35所示。
―――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――
set serveroutput on
declare
tempsal scott.emp.sal%type;
cursor mycursor is
select * from scott.emp
where sal>tempsal;
begin
tempsal:=800;
open mycursor;
end;
―――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――【配套程序位置】:第9章\ cursordefine.sql。
打開游標
要使用創建好的游標,接下來要打開游標,語法結構如下:
open 游標名;
打開游標的過程有以下兩個步驟:
(1)將符合條件的記錄送入內存。
(2)將指針指向第一條記錄。
提取游標數據
要提取游標中的數據,使用fetch命令,語法形式如下。
fetch 游標名 into 變量名1, 變量名2,……;
或
fetch 游標名 into 記錄型變量名;
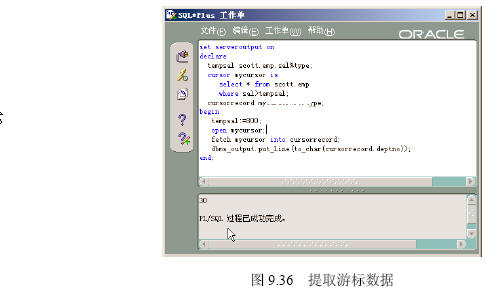
在【SQLPlus Worksheet】中執行下列PL/SQL程序,該程序定義cursorrecord變量是游標mycursor的記錄行變量,在游標mycursor的結果中找到sal字段大於800的第一個記錄,顯示deptno字段的內容。
執行結果如圖9.36所示。
―――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――
set serveroutput on
declare
tempsal scott.emp.sal%type;
cursor mycursor is
select * from scott.emp
where sal>tempsal;
cursorrecord mycursor%rowtype;
begin
tempsal:=800;
open mycursor;
fetch mycursor into cursorrecord;
dbms_output.put_line(to_char(cursorrecord.deptno));
end;
―――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――【配套程序位置】:第9章\ cursorfetch.sql。
關閉游標
使用完游標後,要關閉游標,使用close命令,語法形式如下:
close 游標名;
游標的屬性
游標提供的一些屬性可以幫助編寫PL/SQL程序,游標屬性的使用方法為:游標名[屬性],例如mycursor%isopen,主要的游標屬性如下。
1. %isopen屬性
該屬性功能是測試游標是否打開,如果沒有打開游標就使用fetch語句將提示錯誤。
在【SQLPlus Worksheet】中執行下列PL/SQL程序,該程序利用%isopen屬性判斷游標是否打開。執行結果如圖9.37所示。
―――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――
set serveroutput on
declare
tempsal scott.emp.sal%type;
cursor mycursor is
select * from scott.emp
where sal>tempsal;
cursorrecord mycursor%rowtype;
begin
tempsal:=800;
if mycursor%isopen then
fetch mycursor into cursorrecord;
dbms_output.put_line(to_char(cursorrecord.deptno));
else
dbms_output.put_line('游標沒有打開!');
end if;
end;
―――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――――