oracle壓縮技術分為基本表壓縮(basic table compression),OLTP表壓縮(OLTP table compression),索引壓縮(index compression)和混合列壓縮(hybrid columnar compression (HCC))。
basic compression從9i開始推出,是oracle的默認壓縮方式。OLTP compression是11g開始推出,支持所有類型的DML操作的數據壓縮。壓縮會節省磁盤空間,但可能會增加CPU資源的消耗。本文主要討論常用的basic和LTOP壓縮,索引壓縮和HCC可以參考oracle其它文檔。表壓縮技術適合OLAP系統和OLTP系統中數據變化很小的歷史表,不適合頻繁DML操作的表
1.1 壓縮的原理
以OLTP壓縮為例,引用參考文檔4的說明,原理如下
請看一個 ACCOUNTS 表,它包含以下記錄:
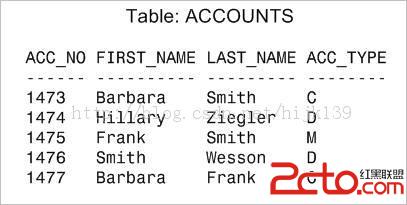
在數據庫內部,假定一個數據庫塊包含上述所有行。

解壓縮的塊看上去是這樣的:記錄中的所有字段(列)都包含數據。壓縮此塊時,數據庫首先計算在所有行中發現的重復值,將這些值移出行外,然後將其放在塊的頭部附近。行中的這些重復值將被替換為一個表示其中每個值的符號。從概念上講,它看上去如下圖所示,您可以看到壓縮前後的塊。
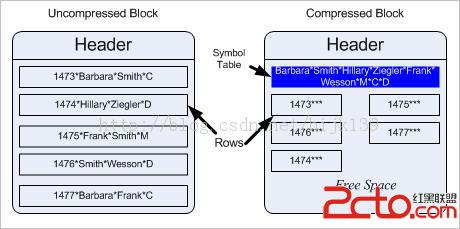
注意這些值是如何從行中取出並放入頂部稱為“符號表”的特殊區域中的。列中的每個值都被分配一個符號,此符號將替代行內的實際值。由於符號所占空間小於實際值,因此記錄大小也遠遠小於初始值。行中的重復數據越多,符號表和塊越緊湊。
由於壓縮作為觸發事件發生,而不是在插入行時發生,因此在正常的 DML 進程中壓縮對性能沒有任何影響。壓縮被觸發後,對 CPU 的需求肯定會變得很高,但在其他任何時間 CPU 影響都為零,因此壓縮也適用於 OLTP 應用程序,這是 Oracle Database 11g 中壓縮的平衡點。
除了減少空間占用外,壓縮數據還將縮短網絡傳輸時間、減少備份空間,並使在 QA 和測試中維護生產數據庫的完整副本變得切實可行。
1.2 basic壓縮
下面通過具體的實驗來看basic壓縮和OLTP壓縮的效果和異同點。
basic compression的6組實驗,來比較各種情況下的表壓縮
?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 sys@MS4ADB3(dtydb5)> select count(*)from test; COUNT(*) ---------- 50000 -- 1.Baseline CTAS create table t1 tablespace users as select * from test where rownum <=50000; -- 2.CTAS with basic compression enabled create table t2 compress basic tablespaceusers as select * from test where rownum <=50000; -- 3.Normal insert into empty table defined as compressed create table t3 compress basic tablespaceusers as select * from test where rownum = 0; insert into t3 select * from test whererownum <= 50000; -- 4.Direct path insert into empty table defined as compressed create table t4 compress basic tablespaceusers as select * from test where rownum = 0; insert /*+append*/ into t4 select * fromtest where rownum <= 50000 -- 5.CTAS without compression, then change to compressed create table t5 tablespace users as select * from test where rownum <=50000; alter table t5 compress basic;?
1 2 3 4 5 6 --- 6. table move compress create table t6 tablespace users as select * from test where rownum <=50000; alter table t6 move compress basic;對表做表分析
?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 execdbms_stats.gather_table_stats('SYS','T1'); execdbms_stats.gather_table_stats('SYS','T2'); execdbms_stats.gather_table_stats('SYS','T3'); execdbms_stats.gather_table_stats('SYS','T4'); execdbms_stats.gather_table_stats('SYS','T5'); execdbms_stats.gather_table_stats('SYS','T6');查詢表占用空間情況
?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 sys@MS4ADB3(dtydb5)> select table_name,blocks, pct_free , compression,compress_for 2 from user_tables 3 where table_name in('T1','T2','T3','T4','T5','T6'); TABLE_NAME BLOCKS PCT_FREE COMPRESSION COMPRESS_FOR ---------------------------------------------------------------------- ---------- ---------------- ------------------------ T1 666 10 DISABLED T2 204 0 ENABLED BASIC T3 622 0 ENABLED BASIC T4 204 0 ENABLED BASIC T5 666 10 ENABLED BASIC T6 204 0 ENABLED BASIC sys@MS4ADB3(dtydb5)> selectsegment_name,bytes/1024 K from dba_segments where segment_name in('T1','T2','T3','T4','T5','T6'); SEGMENT_NA K --------- ---------- T1 6144 T2 2048 T3 5120 T4 2048 T5 6144 T6 2048結果分析:
從上可以看出,
basic compression
在CATS,insert /*+append*/和move compress操作會對數據進行壓縮。而alter table compress操作會修改表的壓縮屬性,但不會對已有數據進行壓縮,對壓縮表做普通的insert操作也不對對數據進行壓縮。壓縮表的PCT_FREE為0,說明oracle設計基本壓縮表的目的就是認為此類表以後會很少修改
1.3 OLTP壓縮
使用OLTP壓縮分別做以下6組實驗
?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 -- 1. Baseline CTAS create table t21 tablespace users as select * from test where rownum <= 50000; -- 2. CTAS with OLTP compress enabled create table t22 compress for OLTP tablespace users as select * from test where rownum <= 50000; -- 3. Normal insert into empty table defined as compressed create table t23 compress for OLTP tablespace users as select * from test where rownum = 0; insert into t23 select * from test where rownum <= 50000; -- 4. Direct path insert into empty table defined as compressed create table t24 compress for OLTP tablespace users as select * from test where rownum = 0; insert /*+append*/ into t24 select * from test where rownum <= 50000; -- 5. CTAS without compression, then change to compressed create table t25 tablespace users as select * from test where rownum <= 50000; alter table t25 compress for OLTP; --- 6. table move compress create table t26 tablespace users as select * from test where rownum <= 50000; alter table t26 move compress for OLTP;表分析
?
1 2 3 4 5 6 exec dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('SYS','T21'); exec dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('SYS','T22'); exec dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('SYS','T23'); exec dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('SYS','T24'); exec dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('SYS','T25'); exec dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('SYS','T26');表占用空間的大小
?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 sys@MS4ADB3(dtydb5)> select table_name,blocks, pct_free , compression, compress_for 2 from user_tables 3 where table_name in ('T21','T22','T23','T24','T25','T26'); TABLE_NAME BLOCKS PCT_FREE COMPRESSION COMPRESS_FOR ------------------------------------------------------------ ---------- ---------- ---------------- ------------------------ T21 666 10 DISABLED T22 225 10 ENABLED OLTP T23 370 10 ENABLED OLTP T24 225 10 ENABLED OLTP T25 666 10 ENABLED OLTP T26 225 10 ENABLED OLTP比較分析
OTLP壓縮實現了對DML操作的壓縮(T23表),主要原理如圖所示,當向空塊插入數據時,數據不壓縮,只有當數據超過一個閥值時,此時oracle才對數據塊進行壓縮,而且可能對同一個數據塊多次壓縮
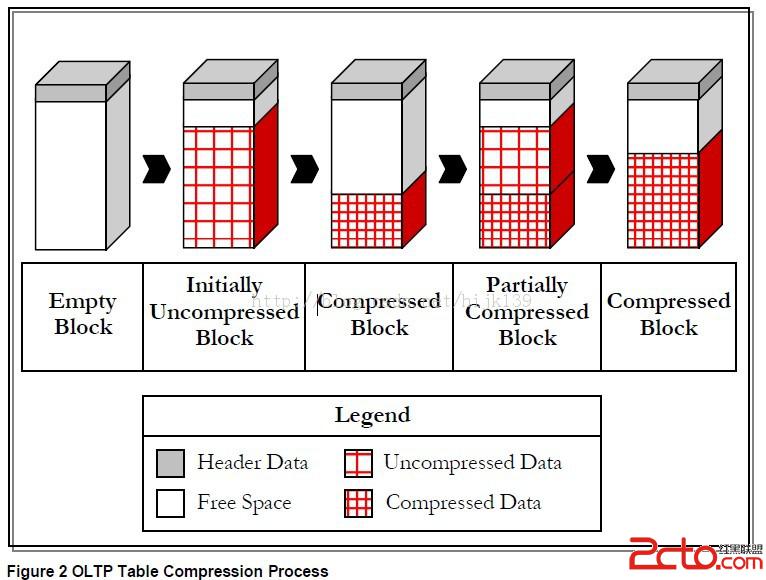
轉化為壓縮表的3方法
1. ALTER TABLE … COMPRESS FOR OLTP
此方法對現有數據不壓縮,對以後的DML語句相關數據進行OLTP壓縮
2. Online Redefinition (DBMS_REDEFINITION)
對現有和以後的數據均壓縮。使用DBMS_REDEFINITION可以在線對表進行操作,可以使用並行操作。分區表的global index是個例外,需要在線重定義之後重建索引
3. ALTER TABLE … MOVE COMPRESS FOR OLTP
對現有和以後的數據均壓縮。在move過程中,會對表加排它(X)鎖,DML操作會被阻塞,可以使用並行提高性能。move操作會導致索引失效,因此move之後需要重建索引。move操作可以改變segment的表空間