工作和學習中常常會遇到一行要分割成多行數據的情況,在此整理一下做下對比。
如果表數據只有一行,則可以直接在原表上直接使用connect by+正則的方法,比如:
select regexp_substr('444.555.666', '[^.]+', 1, level) col
from dual
connect by level <= regexp_count('444.555.666', '\.') + 1
輸出結果:
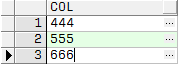
如果數據表存在多行數據需要拆分,也可以在原表上使用connect+正則的方法:
方法一、
with t as
(select '111.222.333' col
from dual
union all
select '444.555.666' col
from dual)
select regexp_substr(col, '[^.]+', 1, level)
from t
connect by level <= regexp_count(col, '\.\') + 1
and col = prior col
and prior dbms_random.value > 0
結果:
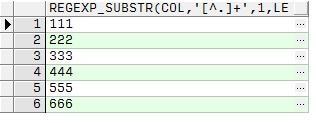
方法二、使用構造的最大行數值關聯原表:
with t as
(select '111.222.333' col
from dual
union all
select '444.555.666' col
from dual)
select regexp_substr(col, '[^.]+', 1, lv)
from t, (select level lv from dual connect by level < 10) b
where b.lv <= regexp_count(t.col, '\.\') + 1
這種方法設置第二個數據集的時候要小於可能的最大值,然後兩數據集做關聯,在做大數據量拆分的時候,這個數值設置得當,拆分行數相對一致的情況下,效率比方法一直接connect by要高。
方法三、使用table函數:
with t as
(select '111.222.333' col
from dual
union all
select '444.555.666' col
from dual)
select column_value
from t,
table(cast(multiset
(select regexp_substr(col, '[^.]+', 1, level) dd
from dual
connect by level <= regexp_count(t.col, '\.\') + 1) as
sys.odcivarchar2list)) a
結果:
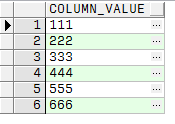
這個方法輸出的列名是固定的,column_value依賴於sys.odcivarchar2list這個類型的輸出,該方法對於大數據量的拆分效率比第二個方法好。
另外需注意,大數據量的拆分時,謹慎使用正則的方法去做,可以使用substr+instr的方式替換正則。
如果以上方法的效率仍然不理想,可考慮使用plsql塊。