最近有個哥們在群裡問,有一個日志,裡面存的是IP地址(一行一個),如何將這些IP快速導入到Redis中。
我剛開始的建議是Shell+redis客戶端。
今天,查看Redis官檔,發現文檔的首頁部分(http://www.redis.io/documentation)有一個專門的主題是講述“Redis Mass Insertion”的,才知道自己的建議很low。
官方給出的理由如下:
Using a normal Redis client to perform mass insertion is not a good idea for a few reasons: the naive approach of sending one command after the other is slow because you have to pay for the round trip time for every command. It is possible to use pipelining, but for mass insertion of many records you need to write new commands while you read replies at the same time to make sure you are inserting as fast as possible.
Only a small percentage of clients support non-blocking I/O, and not all the clients are able to parse the replies in an efficient way in order to maximize throughput. For all this reasons the preferred way to mass import data into Redis is to generate a text file containing the Redis protocol, in raw format, in order to call the commands needed to insert the required data.
大意是:
1> 每個redis客戶端命令之間有往返時延。
2> 只要一部分客戶端支持非阻塞I/O。
個人理解是,redis命令從執行到結果返回,有一定的時延,即便采用多個redis客戶單並發插入,也很難提高吞吐量,因為,只有非阻塞I/O只能針對有限個連接操作。
那麼如何高效的插入呢?
官方在2.6版本推出了一個新的功能-pipe mode,即將支持Redis協議的文本文件直接通過pipe導入到服務端。
說來拗口,具體實現步驟如下:
1. 新建一個文本文件,包含redis命令
SET Key0 Value0 SET Key1 Value1 ... SET KeyN ValueN
如果有了原始數據,其實構造這個文件並不難,譬如shell,python都可以
2. 將這些命令轉化成Redis Protocol。
因為Redis管道功能支持的是Redis Protocol,而不是直接的Redis命令。
如何轉化,可參考後面的腳本。
3. 利用管道插入
cat data.txt | redis-cli --pipe
Shell VS Redis pipe
下面通過測試來具體看看Shell批量導入和Redis pipe之間的效率。
測試思路:分別通過shell腳本和Redis pipe向數據庫中插入10萬相同數據,查看各自所花費的時間。
Shell
腳本如下:
#!/bin/bash for ((i=0;i<100000;i++)) do echo -en "helloworld" | redis-cli -x set name$i >>redis.log done
每次插入的值都是helloworld,但鍵不同,name0,name1...name99999。
Redis pipe
Redis pipe會稍微麻煩一點
1> 首先構造redis命令的文本文件
在這裡,我選用了python
#!/usr/bin/python for i in range(100000): print 'set name'+str(i),'helloworld'
# python 1.py > redis_commands.txt
# head -2 redis_commands.txt
set name0 helloworld set name1 helloworld
2> 將這些命令轉化成Redis Protocol
在這裡,我利用了github上一個shell腳本,
#!/bin/bash
while read CMD; do
# each command begins with *{number arguments in command}\r\n
XS=($CMD); printf "*${#XS[@]}\r\n"
# for each argument, we append ${length}\r\n{argument}\r\n
for X in $CMD; do printf "\$${#X}\r\n$X\r\n"; done
done < redis_commands.txt
# sh 20.sh > redis_data.txt
# head -7 redis_data.txt
*3 $3 set $5 name0 $10 helloworld
至此,數據構造完畢。
測試結果
如下:
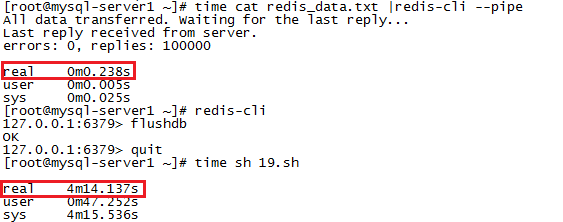
時間消耗完全不是一個量級的。
最後,來看看pipe的實現原理,
即它會盡可能快的將數據發送到Redis服務端,並盡可能快的讀取並解析數據文件中的內容,一旦數據文件中的內容讀取完了,它會發送一個帶有20個字節的字符串的echo命令,Redis服務端即根據此命令來確認數據已插入完畢。
總結:
後續有童鞋好奇,構造redis命令的時間和將命令轉化為protocol的時間,這裡一並貼下:
[root@mysql-server1 ~]# time python 1.py > redis_commands.txt real 0m0.110s user 0m0.070s sys 0m0.040s [root@mysql-server1 ~]# time sh 20.sh > redis_data.txt real 0m7.112s user 0m5.861s sys 0m1.255s
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持。