本文主要為大家介紹緩存技術中的一種Redis的安裝和使用,供大家參考,具體內容如下
一、下載Redis for windows
在網絡中搜索Redis fow windows,就可以下載Redis的壓縮包。解壓包。
會發現其中有32位和64位的不同版本的包,根據需要,使用對應的壓縮包即可。
二、解壓
我使用的是redisbin_x64.zip的壓縮包,將其解壓到redis的文件夾中。
解壓之後,會發現內容只有一些.exe的文件。到這裡,redis就算做好了一半了。
三、配置
在redis下新建一個conf的文件夾,並創建 redis.conf 文本文件。將一下內容復制到配置文件中。
# Redis configuration file example # By default Redis does not run as a daemon. Use 'yes' if you need it. # Note that Redis will write a pid file in /var/run/redis.pid when daemonized. # 是否以後台進程的形式運行,默認為no daemonize no # When run as a daemon, Redis write a pid file in /var/run/redis.pid by default. # You can specify a custom pid file location here. # 如果指定以後台形式執行,則需要指定一個pid文件 pidfile /var/run/redis.pid # Accept connections on the specified port, default is 6379 #監聽端口號 port 6379 # If you want you can bind a single interface, if the bind option is not # specified all the interfaces will listen for connections. # 綁定主機IP # bind 127.0.0.1 # Close the connection after a client is idle for N seconds (0 to disable) # 客戶端空閒超時時間,設置為0,則沒有超時。過了空閒時間,則會將客戶端的連接關閉 timeout 300 # Set server verbosity to 'debug' # it can be one of: # debug (a lot of information, useful for development/testing) # notice (moderately verbose, what you want in production probably) # warning (only very important / critical messages are logged) # 日志記錄等級 loglevel debug # Specify the log file name. Also 'stdout' can be used to force # the demon to log on the standard output. Note that if you use standard # output for logging but daemonize, logs will be sent to /dev/null # 日志記錄方式 logfile stdout # Set the number of databases. The default database is DB 0, you can select # a different one on a per-connection basis using SELECT <dbid> where # dbid is a number between 0 and 'databases'-1 # 可用數據庫數目 databases 16 ################################ SNAPSHOTTING ################################# # # Save the DB on disk: # # save <seconds> <changes> # # Will save the DB if both the given number of seconds and the given # number of write operations against the DB occurred. # # In the example below the behaviour will be to save: # after 900 sec (15 min) if at least 1 key changed # after 300 sec (5 min) if at least 10 keys changed # after 60 sec if at least 10000 keys changed save 900 1 save 300 10 save 60 10000 # Compress string objects using LZF when dump .rdb databases? # For default that's set to 'yes' as it's almost always a win. # If you want to save some CPU in the saving child set it to 'no' but # the dataset will likely be bigger if you have compressible values or keys. # 存儲到本地數據庫時,是否需要壓縮數據 rdbcompression yes # The filename where to dump the DB #本地數據名稱 dbfilename dump.rdb # For default save/load DB in/from the working directory # Note that you must specify a directory not a file name. # 本地數據庫存放路徑 dir ./ ################################# REPLICATION ################################# # Master-Slave replication. Use slaveof to make a Redis instance a copy of # another Redis server. Note that the configuration is local to the slave # so for example it is possible to configure the slave to save the DB with a # different interval, or to listen to another port, and so on. # 當該服務為從服務時,設置主服務的ip地址和端口號 # # slaveof <masterip> <masterport> # If the master is password protected (using the "requirepass" configuration # directive below) it is possible to tell the slave to authenticate before # starting the replication synchronization process, otherwise the master will # refuse the slave request. # 當該服務為從服務時,設置主服務的連接密碼 # # masterauth <master-password> ################################## SECURITY ################################### # Require clients to issue AUTH <PASSWORD> before processing any other # commands. This might be useful in environments in which you do not trust # others with access to the host running redis-server. # # This should stay commented out for backward compatibility and because most # people do not need auth (e.g. they run their own servers). # 連接密碼 # # requirepass foobared ################################### LIMITS #################################### # Set the max number of connected clients at the same time. By default there # is no limit, and it's up to the number of file descriptors the Redis process # is able to open. The special value '0' means no limts. # Once the limit is reached Redis will close all the new connections sending # an error 'max number of clients reached'. # 最大客戶端連接數,默認不設置 # # maxclients 128 # Don't use more memory than the specified amount of bytes. # When the memory limit is reached Redis will try to remove keys with an # EXPIRE set. It will try to start freeing keys that are going to expire # in little time and preserve keys with a longer time to live. # Redis will also try to remove objects from free lists if possible. # # If all this fails, Redis will start to reply with errors to commands # that will use more memory, like SET, LPUSH, and so on, and will continue # to reply to most read-only commands like GET. # # WARNING: maxmemory can be a good idea mainly if you want to use Redis as a # 'state' server or cache, not as a real DB. When Redis is used as a real # database the memory usage will grow over the weeks, it will be obvious if # it is going to use too much memory in the long run, and you'll have the time # to upgrade. With maxmemory after the limit is reached you'll start to get # errors for write operations, and this may even lead to DB inconsistency. # 設置最大內存,達到最大內存設置後,Redis線嘗試清楚已到期或即將到期的key,當此方法處理後,達到最大內存設置,將不能在進行寫入操作。 # # maxmemory <bytes> ############################## APPEND ONLY MODE ############################### # By default Redis asynchronously dumps the dataset on disk. If you can live # with the idea that the latest records will be lost if something like a crash # happens this is the preferred way to run Redis. If instead you care a lot # about your data and don't want to that a single record can get lost you should # enable the append only mode: when this mode is enabled Redis will append # every write operation received in the file appendonly.log. This file will # be read on startup in order to rebuild the full dataset in memory. # # Note that you can have both the async dumps and the append only file if you # like (you have to comment the "save" statements above to disable the dumps). # Still if append only mode is enabled Redis will load the data from the # log file at startup ignoring the dump.rdb file. # # The name of the append only file is "appendonly.log" # # IMPORTANT: Check the BGREWRITEAOF to check how to rewrite the append # log file in background when it gets too big. # 設置Redis服務器在每次操作完成後,是否更新日志操作,如果關閉,可能會在斷電時導致一段時間內的數據丟失, # 因為Redis本身同步數據文件是按照上面的save條件來同步的,所以有的數據會在一段時間內存儲於內存中。 appendonly no # 更新日志文件名 # appendfilename appendonly.aof # The fsync() call tells the Operating System to actually write data on disk # instead to wait for more data in the output buffer. Some OS will really flush # data on disk, some other OS will just try to do it ASAP. # # Redis supports three different modes: # # no: don't fsync, just let the OS flush the data when it wants. Faster. # always: fsync after every write to the append only log . Slow, Safest. # everysec: fsync only if one second passed since the last fsync. Compromise. # # The default is "always" that's the safer of the options. It's up to you to # understand if you can relax this to "everysec" that will fsync every second # or to "no" that will let the operating system flush the output buffer when # it want, for better performances (but if you can live with the idea of # some data loss consider the default persistence mode that's snapshotting). # 更新日志條件,有三個可選值: appendfsync always # appendfsync everysec # appendfsync no ############################### ADVANCED CONFIG ############################### # Glue small output buffers together in order to send small replies in a # single TCP packet. Uses a bit more CPU but most of the times it is a win # in terms of number of queries per second. Use 'yes' if unsure. #glueoutputbuf yes # Use object sharing. Can save a lot of memory if you have many common # string in your dataset, but performs lookups against the shared objects # pool so it uses more CPU and can be a bit slower. Usually it's a good # idea. # # When object sharing is enabled (shareobjects yes) you can use # shareobjectspoolsize to control the size of the pool used in order to try # object sharing. A bigger pool size will lead to better sharing capabilities. # In general you want this value to be at least the double of the number of # very common strings you have in your dataset. # # WARNING: object sharing is experimental, don't enable this feature # in production before of Redis 1.0-stable. Still please try this feature in # your development environment so that we can test it better. # shareobjects no # shareobjectspoolsize 1024 # 是否使用虛擬內存 #vm-enabled no; # 虛擬內存文件路徑,不能多個redis共享 # vm-swap-file /tmp/redis.swap # 將所有大於vm-max-memory 的數據存入虛擬內存。無論vm-max-memory值大小,所有的索引數據都是內存數據。 # 如果將vm-max-memory設置為0,則所有的數據都存放在磁盤。 # vm-max-memory 0
四、啟動redis服務器
使用一下命令啟動 redis服務器。
redis-server.exe conf/redis.conf
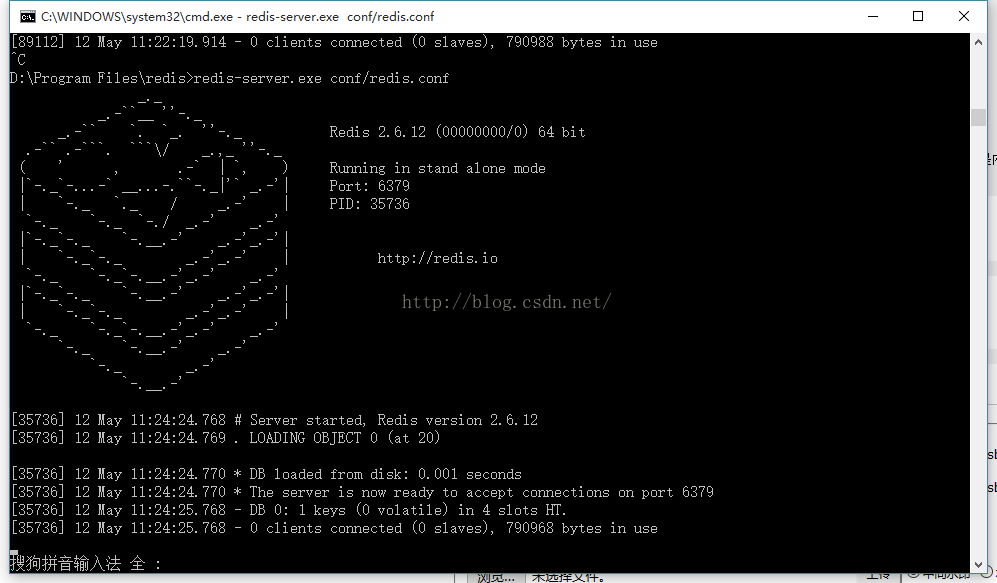
啟動成功之後,你會看到如下的提示:
五、連接redis服務器
使用redis自帶的命令,能夠連接服務器。
redis-cli.exe -h localhost -p 6379
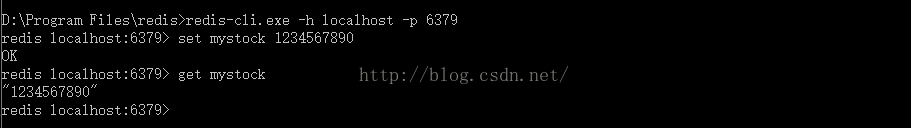
連接成功之後,會提示以下內容:
這個時候,你就能夠使用redis的一下指令操作數據。其他指令,請在網上具體查看一下。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助。