Flush操作是將HBase中的數據存到硬盤上的過程,具體的flush的流程圖如下,本文主要簡要分析flush的過程相關源碼。
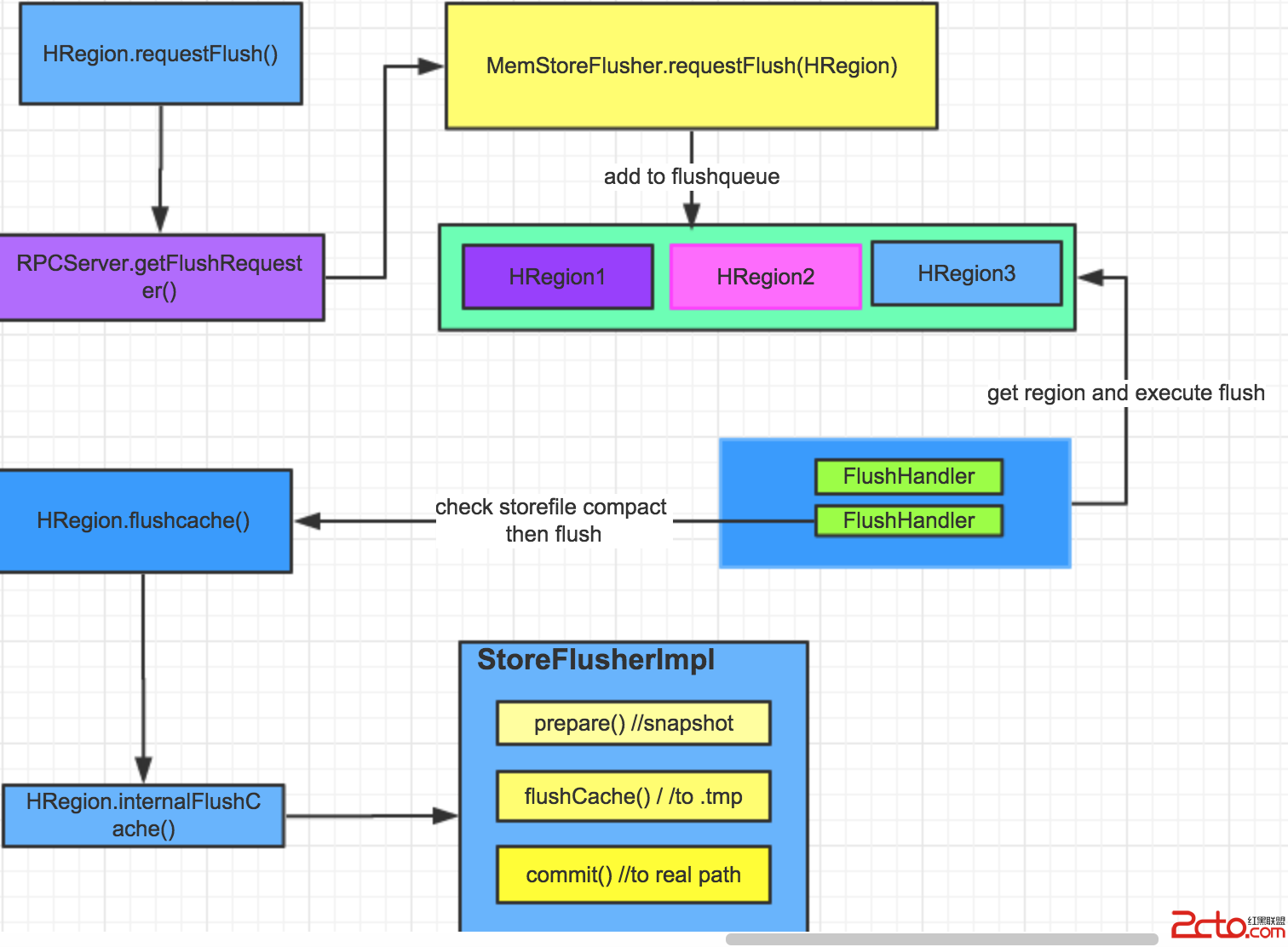
每當HRegion完成數據插入的操作的時候,就會進行檢查此時是否需要進行一次flush,flush是將HRegion緩存的數據存儲到磁盤的過程:
long addedSize = doMiniBatchMutation(batchOp);
long newSize = this.addAndGetGlobalMemstoreSize(addedSize);
if (isFlushSize(newSize)) {
requestFlush();
}
本文主要分析flush的過程以及涉及到得相關數據結構,在requestFlush內部調用:
this.rsServices.getFlushRequester().requestFlush(this);實際是調用了MemStoreFlusher具體執行flush的操作:
public void requestFlush(HRegion r) {
synchronized (regionsInQueue) {
if (!regionsInQueue.containsKey(r)) {
// This entry has no delay so it will be added at the top of the flush
// queue. It'll come out near immediately.
FlushRegionEntry fqe = new FlushRegionEntry(r);
this.regionsInQueue.put(r, fqe);
this.flushQueue.add(fqe);
}
}
}
MemStoreFlushRequeter有兩個數據結構管理者需要flush的任務,private BlockingQueue
到這裡flush request的請求就提交結束了,接下來等待MemStore中的FlushHander線程取出region並執行flush的任務。
Flush的任務執行前期准備1.FlushHandler從flushQueue中取出FlushRegionEntry並執行
flushRegion(final FlushRegionEntry fqe)
這裡首先判斷當前region中是否含有過多的storefile的文件,如果是的話,需要首先進行storefile的合並操作(這裡有必要解釋一下HRegion中的數據組織),然後重新加入隊列,否則的話直接對region執行flush操作:
isTooManyStoreFiles(region)
this.server.compactSplitThread.requestSystemCompaction(
region, Thread.currentThread().getName());
this.flushQueue.add(fqe.requeue(this.blockingWaitTime / 100));
else
return flushRegion(region, false);
2.flushRegion函數內部的主要執行邏輯如下,首先notifyFlushRequest只是進行一些flush線程數量的統計,region.flashcache具體負責flush的工作。執行完之後會根據返回值進行相關的輔助操作
notifyFlushRequest(region, emergencyFlush);
HRegion.FlushResult flushResult = region.flushcache();
boolean shouldCompact = flushResult.isCompactionNeeded();
// We just want to check the size
boolean shouldSplit = region.checkSplit() != null;
if (shouldSplit) {
this.server.compactSplitThread.requestSplit(region);
} else if (shouldCompact) {
server.compactSplitThread.requestSystemCompaction(
region, Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
if (flushResult.isFlushSucceeded()) {
long endTime = EnvironmentEdgeManager.currentTime();
server.metricsRegionServer.updateFlushTime(endTime - startTime);
}
Flush的任務執行過程flushcahe內部調用 FlushResult fs = internalFlushcache(status);實際執行flush操作,StoreFlushContext的實現為StoreFlusherImpl,為每個HStore建一個StoreFlusherImpl,它為對應的HStore執行著具體非flush的操作。flush的具體實現包括三個步驟:
1.快照
public void prepare() {
this.snapshot = memstore.snapshot();
this.cacheFlushCount = snapshot.getCellsCount();
this.cacheFlushSize = snapshot.getSize();
committedFiles = new ArrayList(1);
}
2.將memestore中的數據寫入.tmp文件中
public void flushCache(MonitoredTask status) throws IOException {
tempFiles = HStore.this.flushCache(cacheFlushSeqNum, snapshot, status);
}
3.將.tmp文件寫入對應的cf下面的對應的文件中去,並用StoreFile保存相應的HFile的文件信息
public boolean commit(MonitoredTask status) throws IOException {
if (this.tempFiles == null || this.tempFiles.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
List storeFiles = new ArrayList(this.tempFiles.size());
for (Path storeFilePath : tempFiles) {
try {
storeFiles.add(HStore.this.commitFile(storeFilePath, cacheFlushSeqNum, status));
} catch (IOException ex) {
LOG.error("Failed to commit store file " + storeFilePath, ex);
// Try to delete the files we have committed before.
for (StoreFile sf : storeFiles) {
Path pathToDelete = sf.getPath();
try {
sf.deleteReader();
} catch (IOException deleteEx) {
LOG.fatal("Failed to delete store file we committed, halting " + pathToDelete, ex);
Runtime.getRuntime().halt(1);
}
}
throw new IOException("Failed to commit the flush", ex);
}
}
for (StoreFile sf : storeFiles) {
if (HStore.this.getCoprocessorHost() != null) {
HStore.this.getCoprocessorHost().postFlush(HStore.this, sf);
}
committedFiles.add(sf.getPath());
}
HStore.this.flushedCellsCount += cacheFlushCount;
HStore.this.flushedCellsSize += cacheFlushSize;
// Add new file to store files. Clear snapshot too while we have the Store write lock.
return HStore.this.updateStorefiles(storeFiles, snapshot.getId());
}
至此HBase的flush的操作過程就完成了。