1 struct FileMetaData {
2 int refs;
3 int allowed_seeks; // Seeks allowed until compaction
4 uint64_t number;
5 uint64_t file_size; // File size in bytes
6 InternalKey smallest; // Smallest internal key served by table
7 InternalKey largest; // Largest internal key served by table
8
9 FileMetaData() : refs(0), allowed_seeks(1 << 30), file_size(0) { }
10 };
number為一個遞增的序號,用於創建文件名,allowed_seeks作者有提到,是當前文件在Compaction到下一級之前允許Seek的次數,這個次數和文件大小相關,文件越大,Compaction之前允許Seek的次數越多,這個Version備忘時也會提。 BuildTable方法中真正做事的時TableBuilder,通過調用Add方法將所有記錄添加到數據表中,完成SSTable創建。 TableBuilder主要做了如下幾件事: 創建Index Block:用於Data Block的快速定位 將數據分為一個個的Data Block 如文件需要壓縮,執行壓縮動作 依次寫入Data Block、Meta Block、Index Block、Footer Block,形成完整的SSTable文件結構 其中階段1-3由Add方法完成,階段4由Finish方法完成,先來看Add方法:
1 void TableBuilder::Add(const Slice& key, const Slice& value) {
2 Rep* r = rep_;
3 assert(!r->closed);
4 if (!ok()) return;
5 if (r->num_entries > 0) {
6 assert(r->options.comparator->Compare(key, Slice(r->last_key)) > 0);
7 }
8
9 //Index Block:Data Block的索引元數據。
10 if (r->pending_index_entry) {
11 assert(r->data_block.empty());
12 r->options.comparator->FindShortestSeparator(&r->last_key, key);
13 std::string handle_encoding;
14 r->pending_handle.EncodeTo(&handle_encoding);
15 r->index_block.Add(r->last_key, Slice(handle_encoding));
16 r->pending_index_entry = false;
17 }
18
19 r->last_key.assign(key.data(), key.size());
20 r->num_entries++;
21 r->data_block.Add(key, value);
22
23 const size_t estimated_block_size = r->data_block.CurrentSizeEstimate();
24 if (estimated_block_size >= r->options.block_size) {
25 Flush(); //超過單數據塊大小,寫入文件。
26 }
27 }
Add方法創建Data Block、IndexBlock,DataBlcok通過Flush刷入磁盤文件。 再來看Finish方法:
1 Status TableBuilder::Finish() {
2 //Data Block
3 Rep* r = rep_;
4 Flush();
5
6 assert(!r->closed);
7 r->closed = true;
8
9 //Meta Block
10 BlockHandle metaindex_block_handle;
11 BlockHandle index_block_handle;
12 if (ok())
13 {
14 BlockBuilder meta_index_block(&r->options);
15 // TODO(postrelease): Add stats and other meta blocks
16 WriteBlock(&meta_index_block, &metaindex_block_handle);
17 }
18
19 //Index Block
20 if (ok()) {
21 if (r->pending_index_entry) {
22 r->options.comparator->FindShortSuccessor(&r->last_key);
23 std::string handle_encoding;
24 r->pending_handle.EncodeTo(&handle_encoding);
25 r->index_block.Add(r->last_key, Slice(handle_encoding));
26 r->pending_index_entry = false;
27 }
28 WriteBlock(&r->index_block, &index_block_handle);
29 }
30
31 //Footer
32 if (ok())
33 {
34 Footer footer;
35 footer.set_metaindex_handle(metaindex_block_handle); //
36 footer.set_index_handle(index_block_handle);
37 std::string footer_encoding;
38 footer.EncodeTo(&footer_encoding);
39 r->status = r->file->Append(footer_encoding);
40 if (r->status.ok()) {
41 r->offset += footer_encoding.size();
42 }
43 }
44 return r->status;
45 }
Finish依次寫入:尚未寫入的最後一塊Data Block及Meta Block、Index Block、Footer。Meta Block暫未使用,Footer則保存了meta block、index block的位置信息。 Block Data Block、Meta Block、Index Block是業務劃分,分別代表用戶數據塊、元數據塊及用戶數據索引塊。其存儲格式均為Block結構:
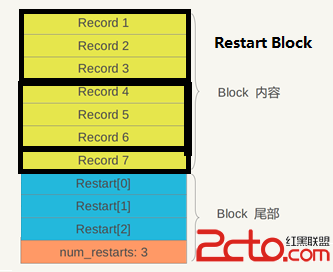 Record代表一條數據,藍色及紅色部分(統一稱作”重啟點”)為附加信息,而這些是做什麼的呢?兩點:性能優化、節省空間。
我們先來看Restart列表的構建邏輯:
Record代表一條數據,藍色及紅色部分(統一稱作”重啟點”)為附加信息,而這些是做什麼的呢?兩點:性能優化、節省空間。
我們先來看Restart列表的構建邏輯:
1 void BlockBuilder::Add(const Slice& key, const Slice& value) {
2 Slice last_key_piece(last_key_);
3 ......
4 size_t shared = 0;
5 if (counter_ < options_->block_restart_interval) {
6 // See how much sharing to do with previous string
7 const size_t min_length = std::min(last_key_piece.size(), key.size());
8 while ((shared < min_length) && (last_key_piece[shared] == key[shared])) {
9 shared++;
10 }
11 }
12 else { //restart時保存完整的key值
13 // Restart compression
14 restarts_.push_back(buffer_.size());
15 counter_ = 0;
16 }
17 const size_t non_shared = key.size() - shared;
18
19 //Record信息
20 // shared size | no shared size | value size | no shared key data | value data
21 // Add "<shared><non_shared><value_size>" to buffer_
22 PutVarint32(&buffer_, shared);
23 PutVarint32(&buffer_, non_shared);
24 PutVarint32(&buffer_, value.size());
25 // Add string delta to buffer_ followed by value
26 buffer_.append(key.data() + shared, non_shared);
27 buffer_.append(value.data(), value.size());
28
29 // Update state
30 last_key_.resize(shared);
31 last_key_.append(key.data() + shared, non_shared);
32 assert(Slice(last_key_) == key);
33 counter_++;
34 }
每隔一定間隔(block_restart_interval)Record就會創建一個新的重啟點,重啟點內容為當前block的大小,即重啟點在block內的偏移。
每當添加一個新的重啟點時,重啟點指向位置的Record中一定保存了完整的key值(shared size = 0),隨後的Record中保存的key值僅為和上一個Record的差異值。因為Key在Block中是有序排列的,所以相鄰key值重疊區域節省的空間還是非常可觀的。
基於上述實現,問題來了:當需要定位一條記錄時,因為record中key的信息是不完整的,僅包含了和上一條的差異項,但上一條記錄本身也只包含了和再上一條的差異項,那麼定位一條記錄時如何做key比較?如果需要一直向上查找完成key值拼接,性能上會不會有損傷?
分析這個問題就要了解重啟點的定位:Block的一級索引,SSTable的二級索引(Index Block是SSTable的一級索引)。本文將每個重啟點記錄位置所屬的Record列表稱為一個Restart Block
假設每條record記錄的都是完整的key值時,從SSTable中查找一條記錄的工作流如下:
根據Key值從Index Block中找到所屬的Data Block
根據Key值從“重啟點”列表中找到所屬的Restart Block,從Restart Block的起始位置進行key值比較,找到正確的記錄。
在上述流程中,我們必定會先找到一個Restart Point,隨後進行key值比較,而Restart Point記錄本身包含了完整的key值信息,後續key值均可基於此key得到。
Restart列表本身做為索引,提升了查找性能,而key值存儲的小技巧又降低了空間使用率,在不損傷性能的情況小降低空間利用率,這是一個很好的例子。
即使這樣,作者覺得還不夠,空間利用率還可以進一步優化,並且不損傷任何讀取數據的性能。
做法和Restart列表的做法類似,是在Index Block中,通過調用FindShortestSeparator / FindShortSuccessor方法實現。
1 // If *start < limit, changes *start to a short string in [start,limit). 2 // Simple comparator implementations may return with *start unchanged, 3 // i.e., an implementation of this method that does nothing is correct. 4 virtual void FindShortestSeparator(std::string* start, const Slice& limit) const = 0; 5 6 // Changes *key to a short string >= *key. 7 // Simple comparator implementations may return with *key unchanged, 8 // i.e., an implementation of this method that does nothing is correct. 9 virtual void FindShortSuccessor(std::string* key) const = 0;
FindShortestSeparator找到start、limit之間最短的key值,如“helloworld”和”hellozoomer”之間最短的key值可以是”hellox”。FindShortSuccessor則更極端,用於找到比key值大的最小key,如傳入“helloworld”,返回的key值可能是“i”而已。